





TRAX CR
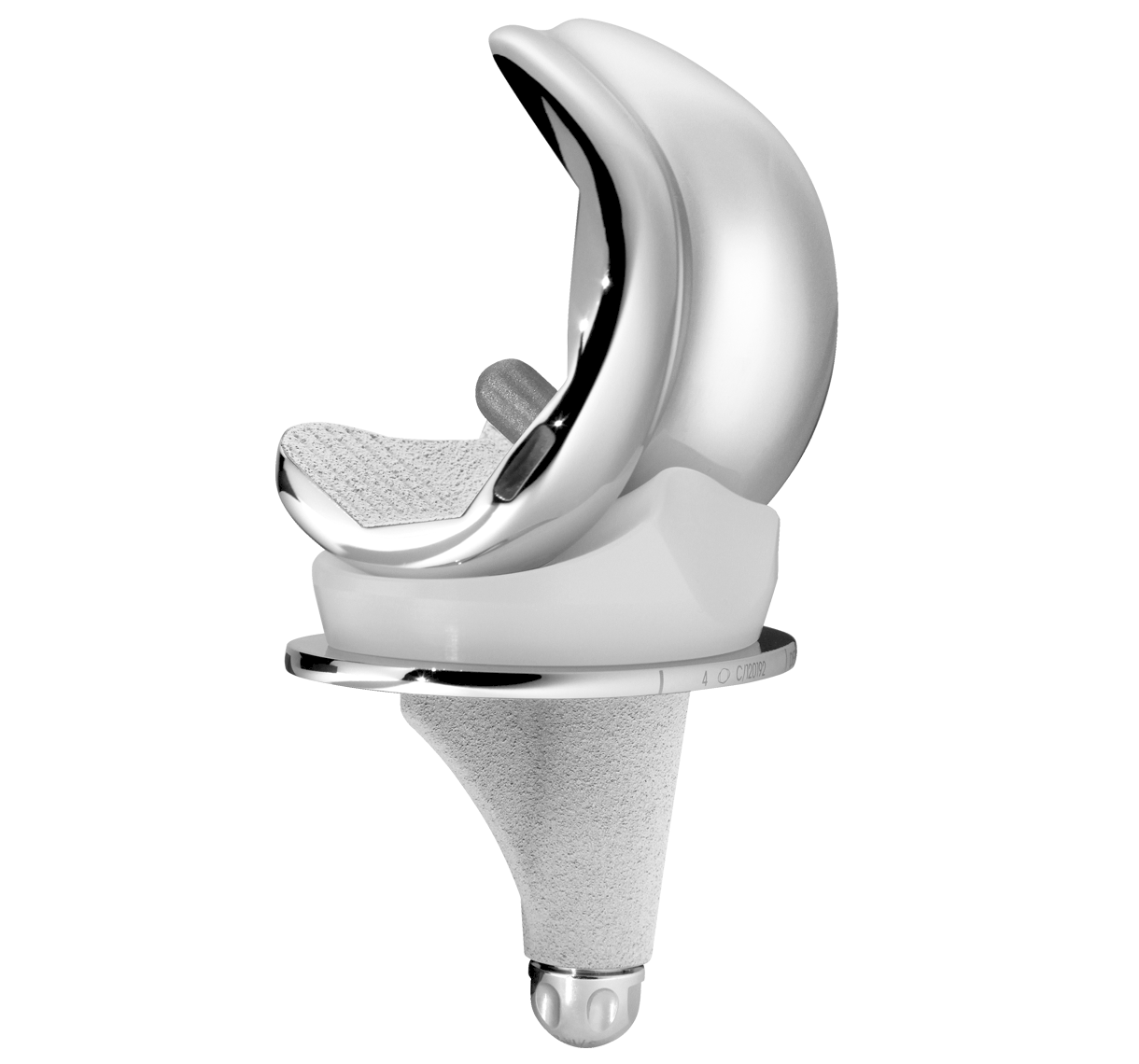
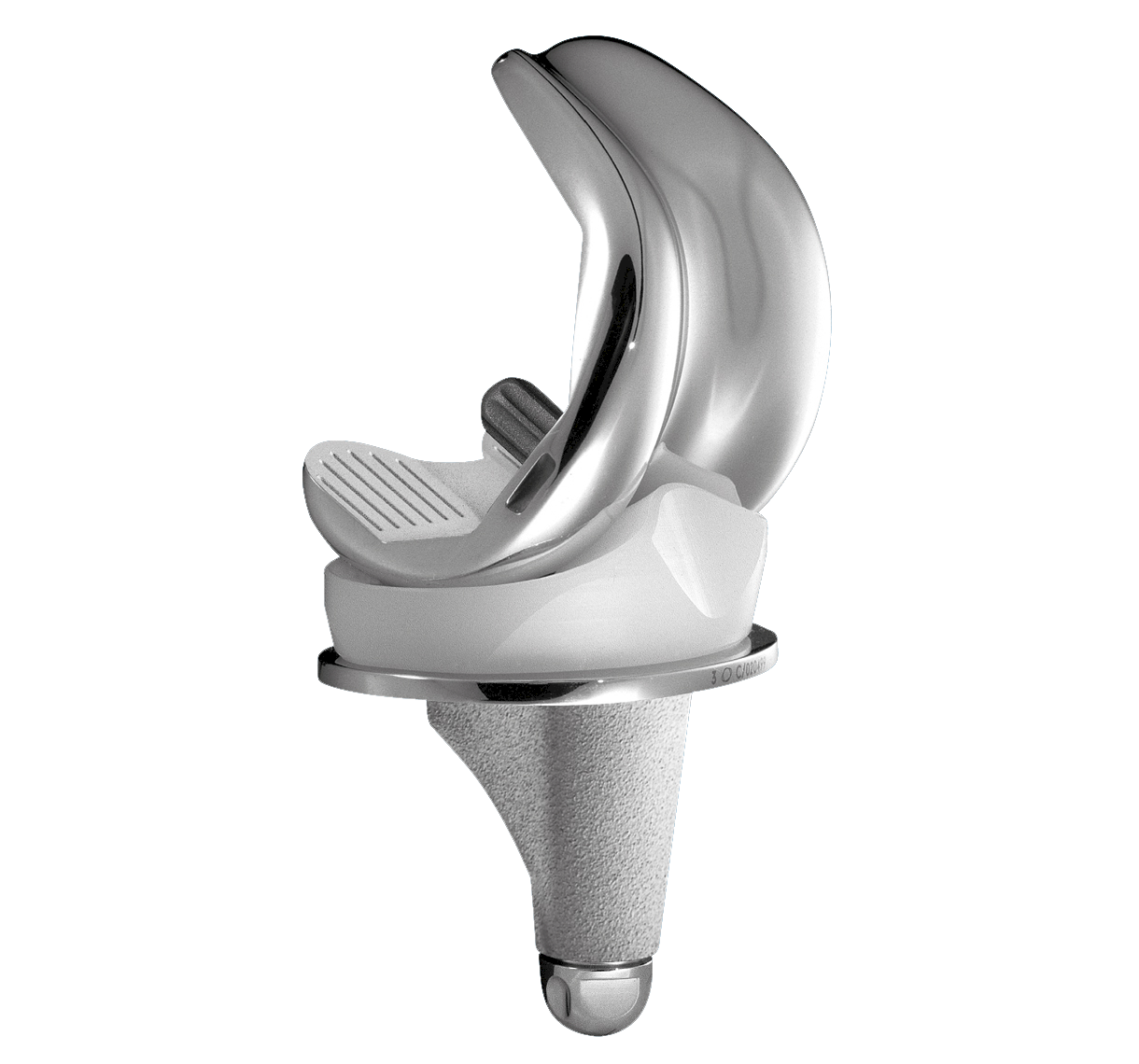
TRAX CR is a primary total knee prosthesis:
- Fixed bearing
- Cruciate Retaining
- Cemented
“Some devices may not be approved in your country, please contact your local distributor for further information”
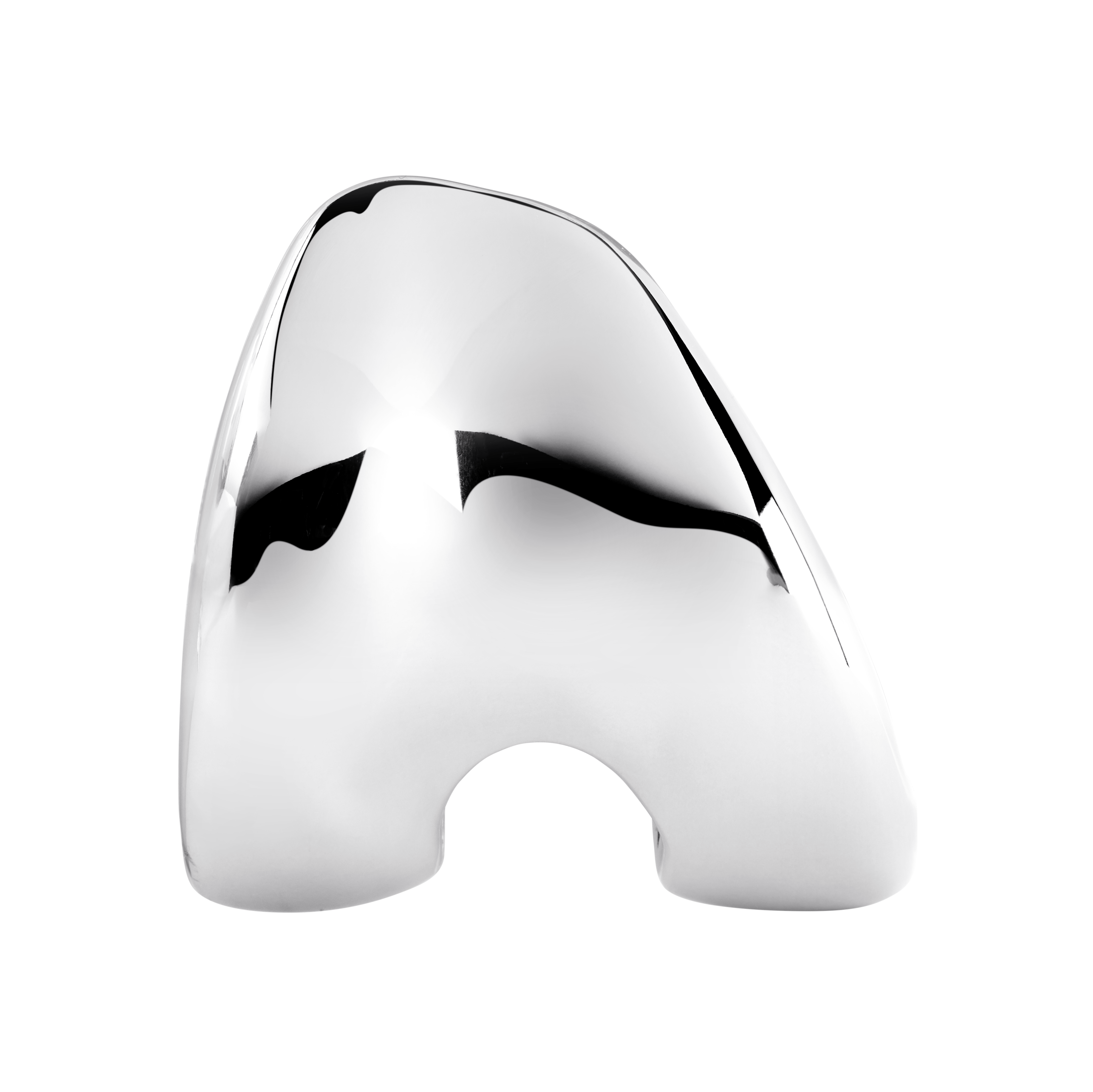

Trochlear groove is angled 6°
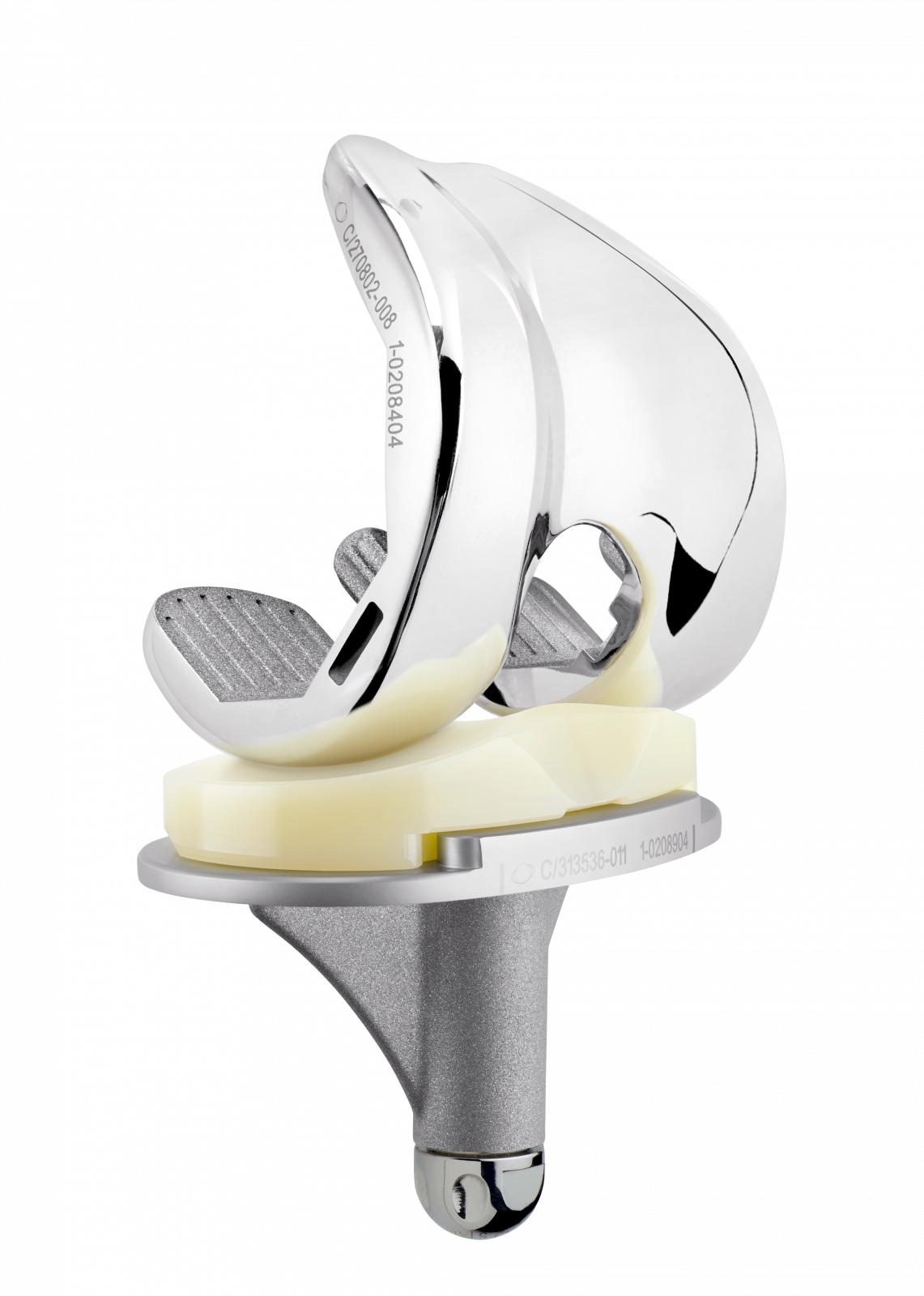
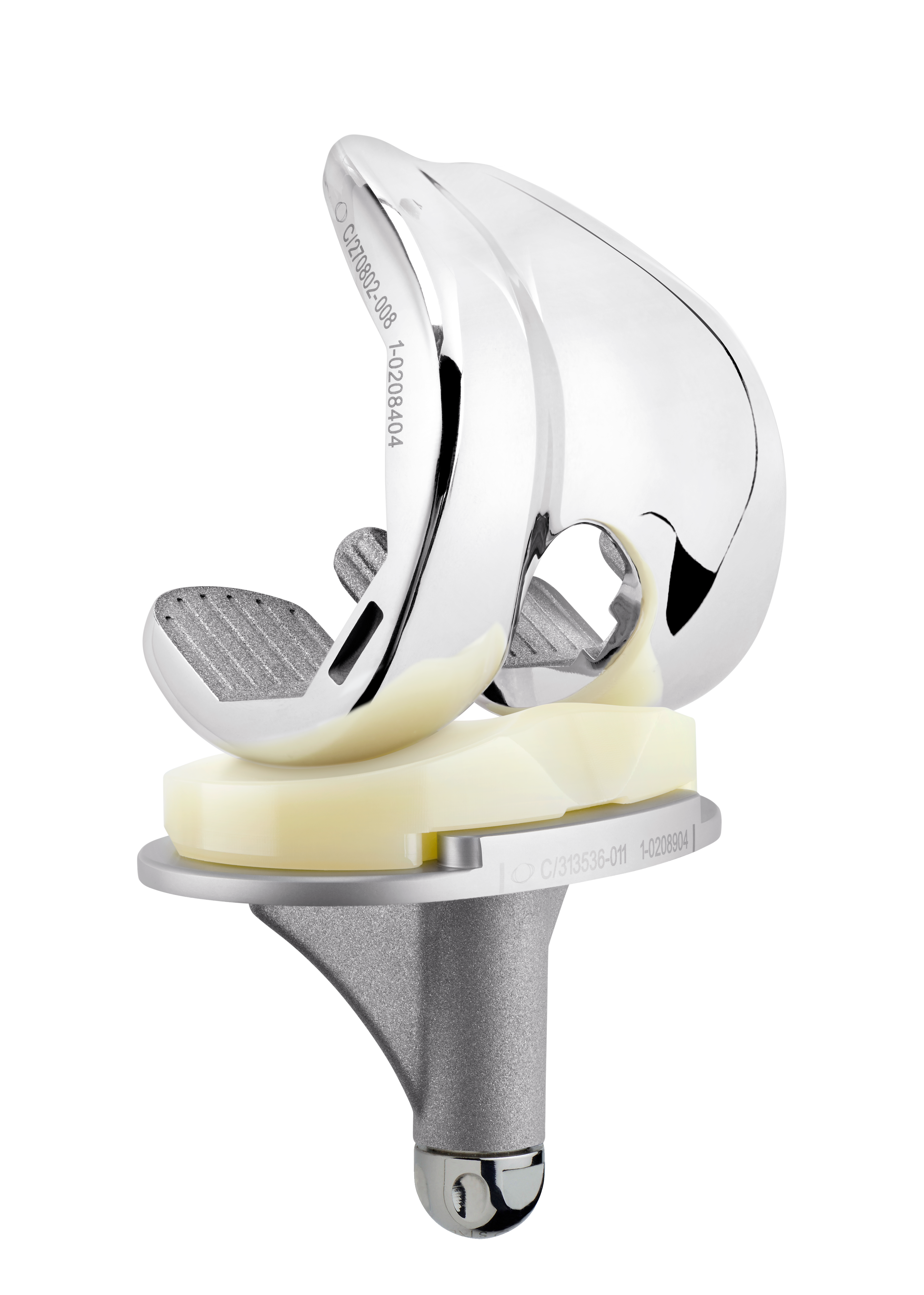
The TRAX femoral component utilises an anatomical lateralised trochlear groove designed to replicate native anatomic patella motion throughout the range after TKR. [1] [2]
Cemented patellar implant available
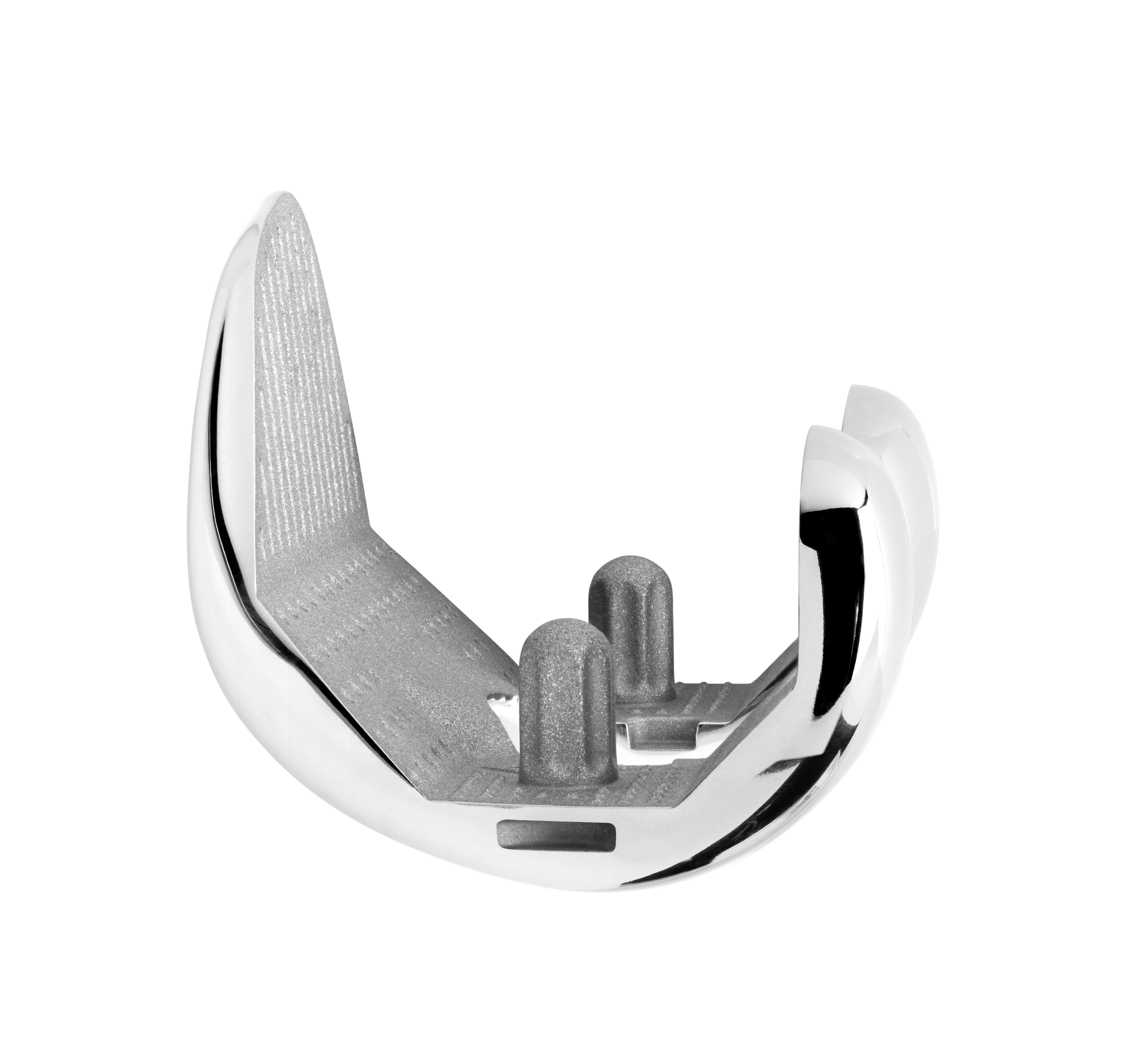

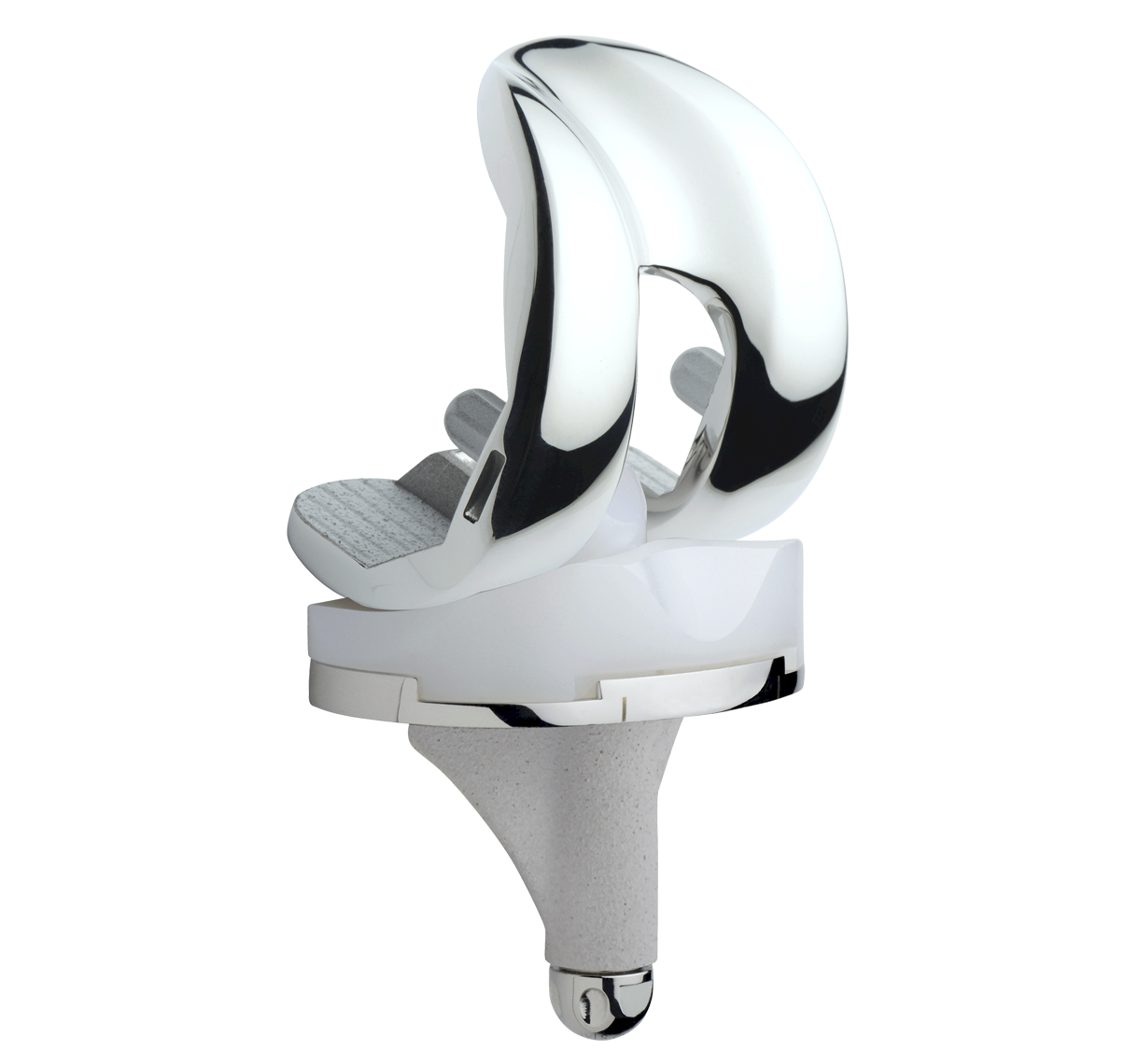
The TRAX knee system incorporates a single radius design during the main flexion arc from 0º to 90º offering patients a more natural motion. Deep flexion is incorporated by a reduced radii on the posterior condyles to ensure a maximum of flexion.
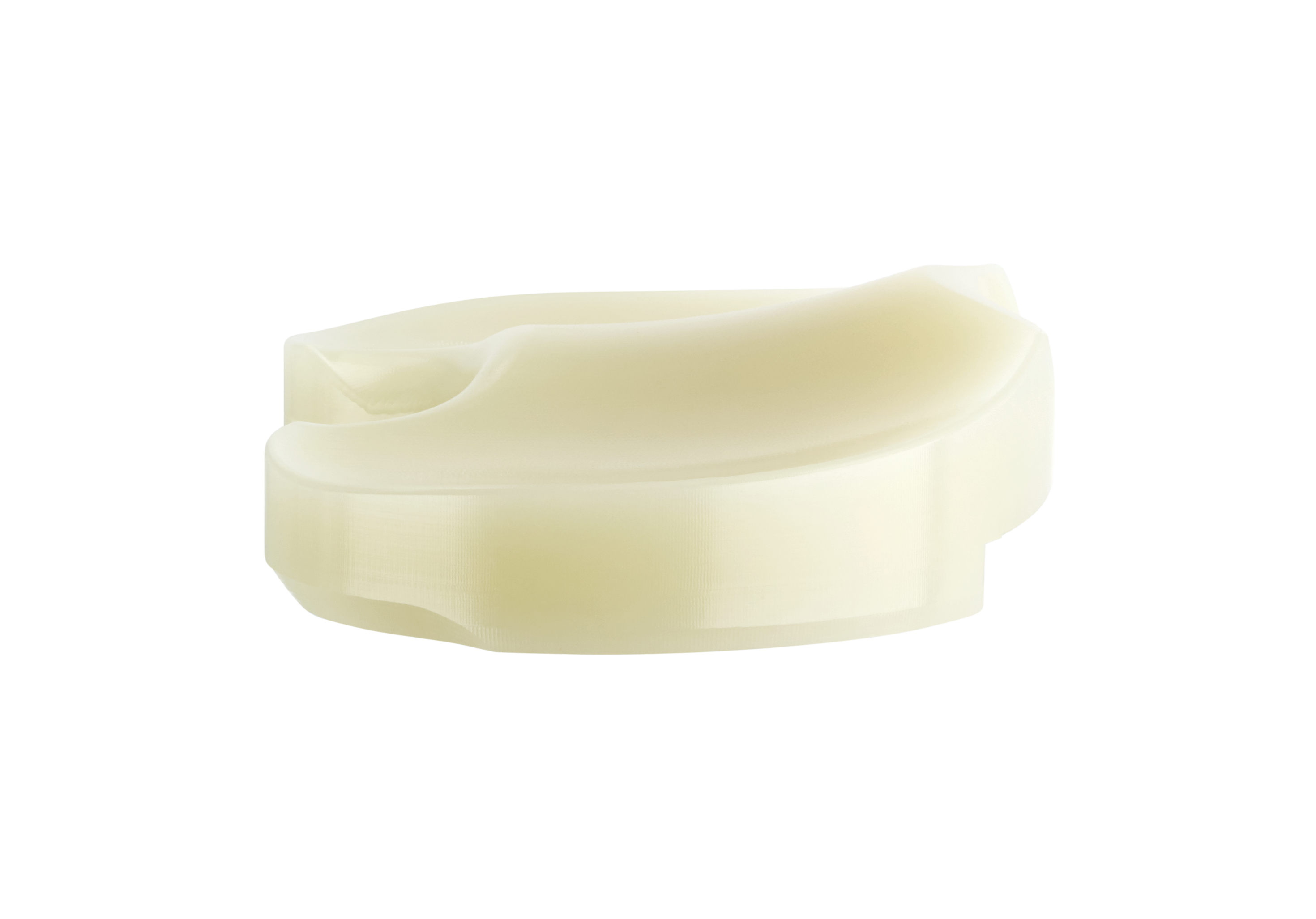

The TRAX system offers AXPe, highly cross-linked polyethylene mixed with vitamin E for all articulating surfaces: tibial insert and patella. AXPe uses high quality materials with verified and validated manufacturing processes.
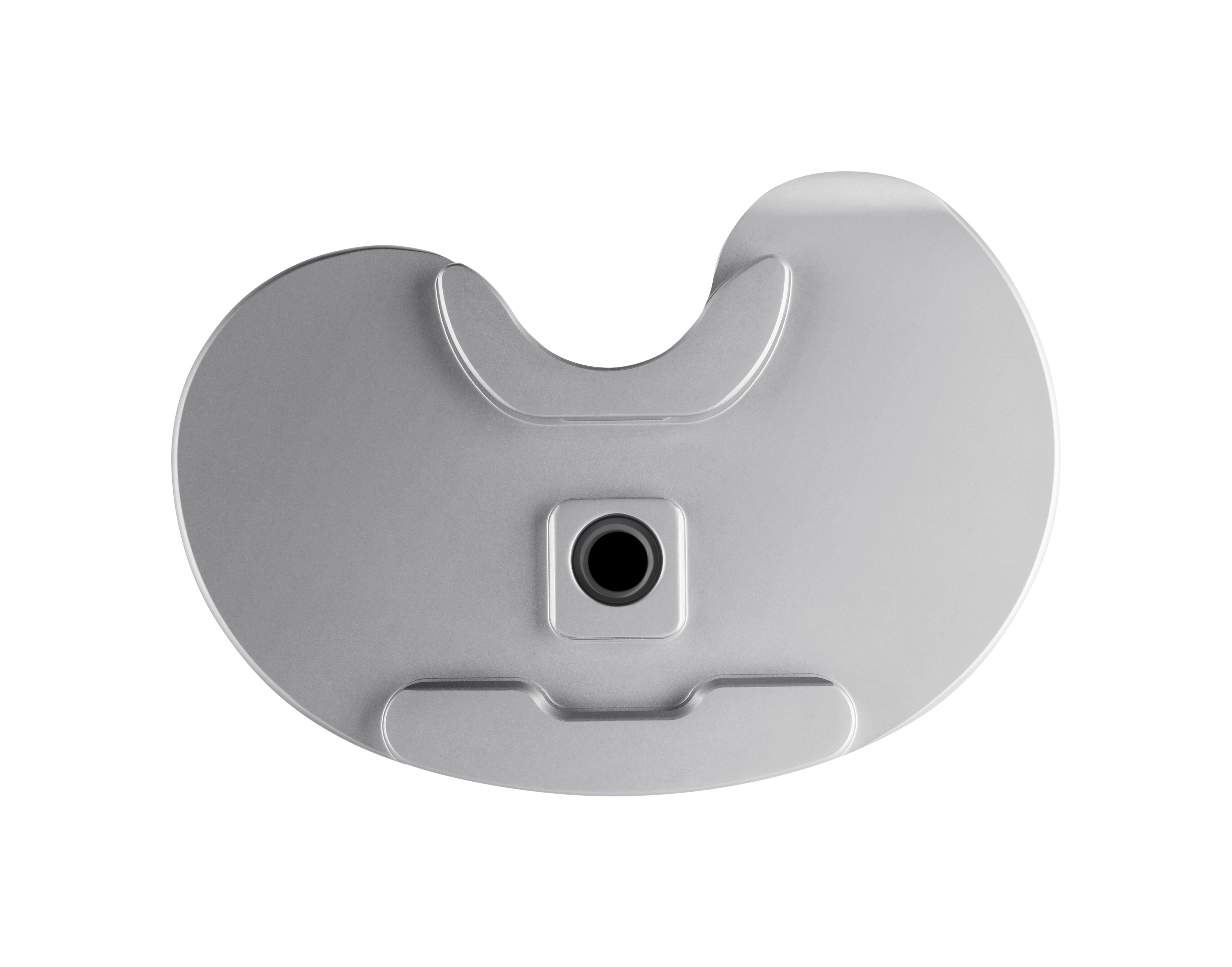

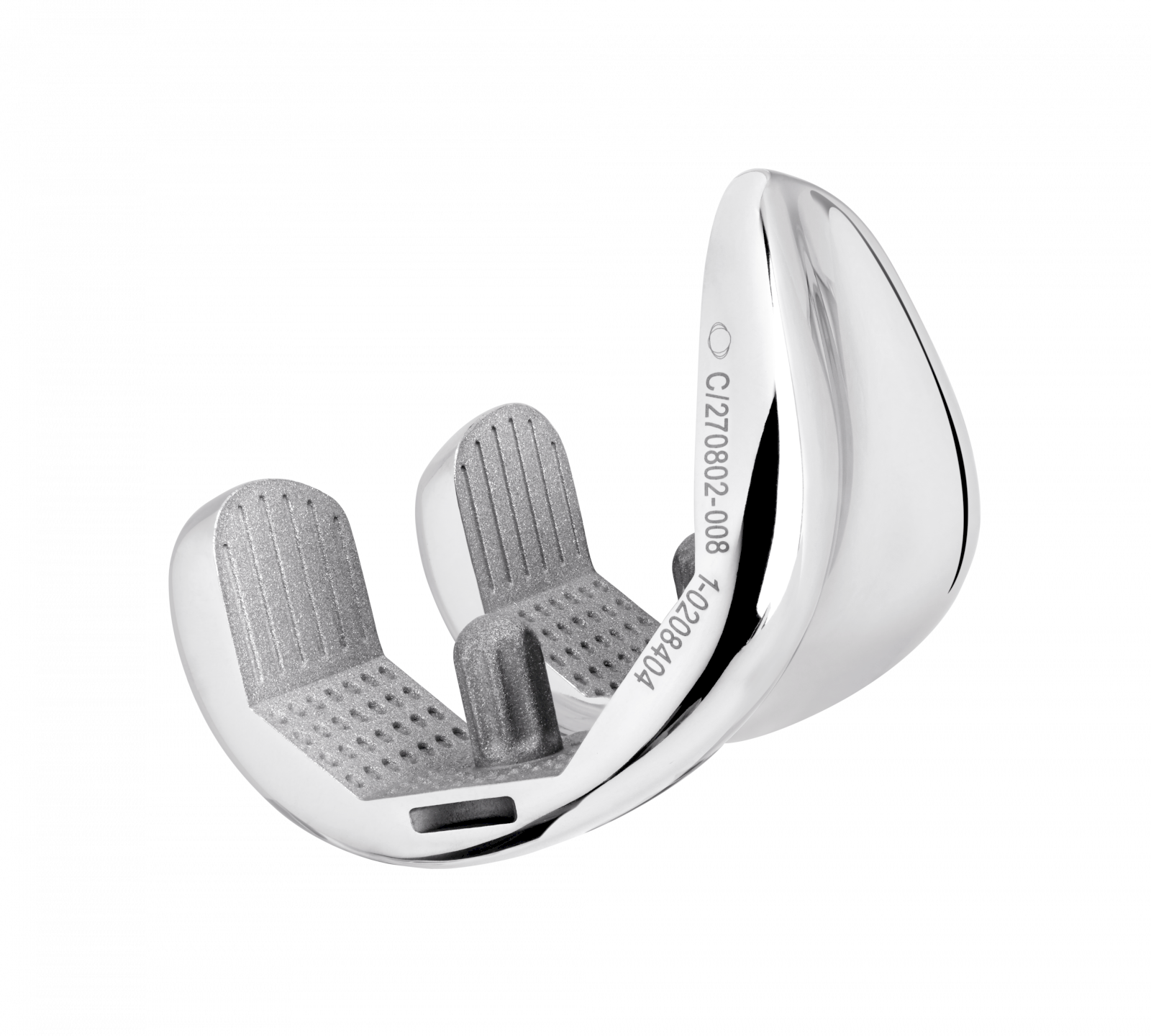
The TRAX knee system’s asymmetric baseplate has been designed with surgeons to ensure uncompromising bone coverage whilst enabling surgeons to optimise tibial rotation. [3] [4]
The TRAX CR instrumentation is focused on efficiency with a limited number of trays.
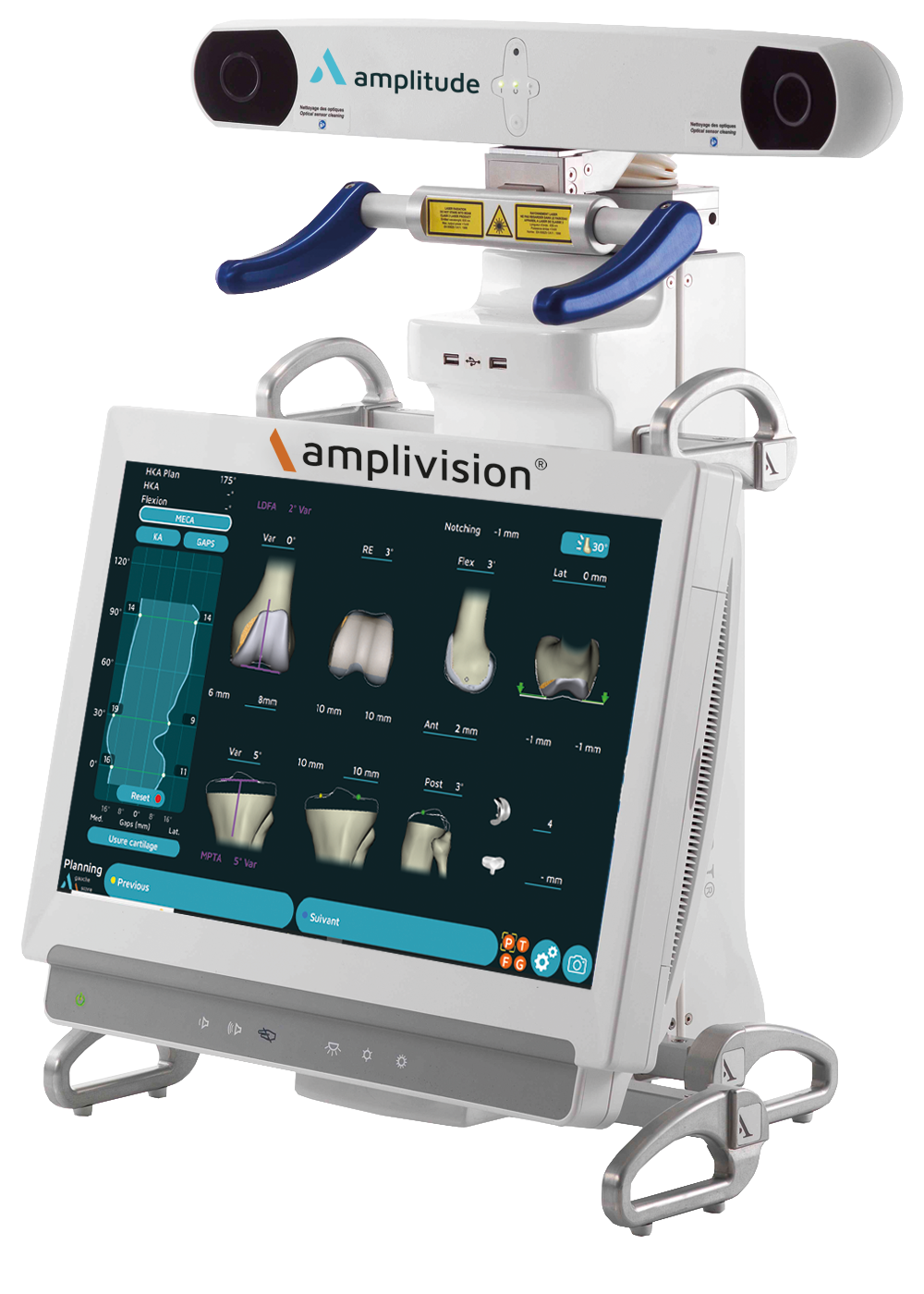
It can be used with the amplivision system and the last generation of software that includes Personalized Approach based on bone morphing and ligament balancing.
[1] Matz J, Lanting BA, Howard JL. Understanding the patellofemoral joint in total knee arthroplasty. Can J Surg. 2019;62(1):57-65. doi:10.1503/cjs.001617
[2] Kainz, H., Reng, W., Augat, P. et al. Influence of total knee arthroplasty on patellar kinematics and contact characteristics. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 36, 73–78 (2012).
[3] Nicoll D, Rowley DI. 2010. “Internal rotational error of the tibial component is a major cause of pain after total knee replacement.” The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume, 92(9): 1238–1244.
[4] MacDessi, S. J “Getting the Tibia Right! Alignment, Coverage and Design”

Femoral components
Cemented: 9 sizes R&L
Inserts
9 sizes and 6 thicknesses: 10, 11, 12, 14, 16 and 18 mm
Tibial components
Cemented: 9 sizes R&L
Patellas
Onset patellar implant - cemented: Ø 30, 33, 36, 39 mm
Stem
Ø 10 mm Lgth 75 mm