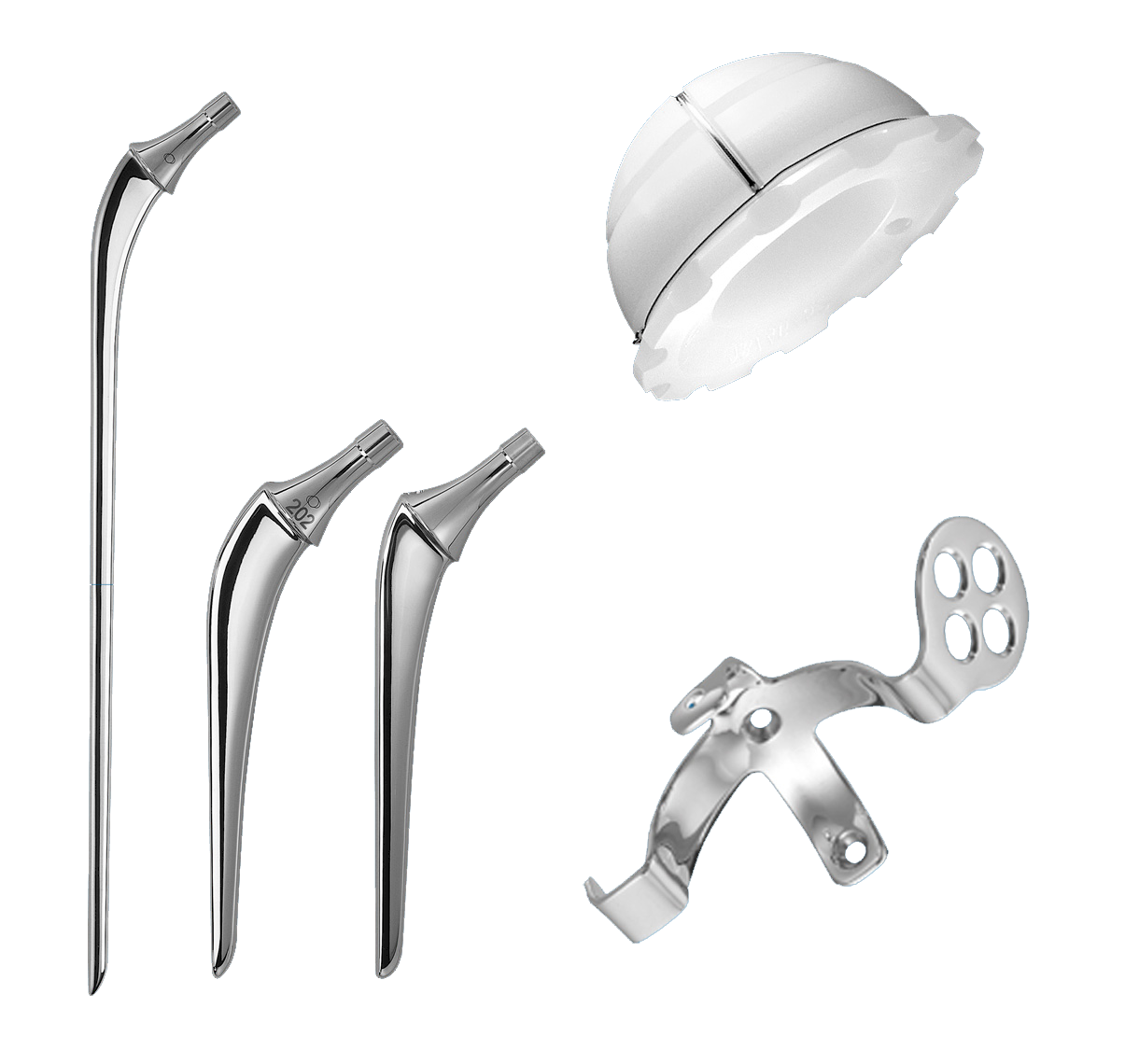

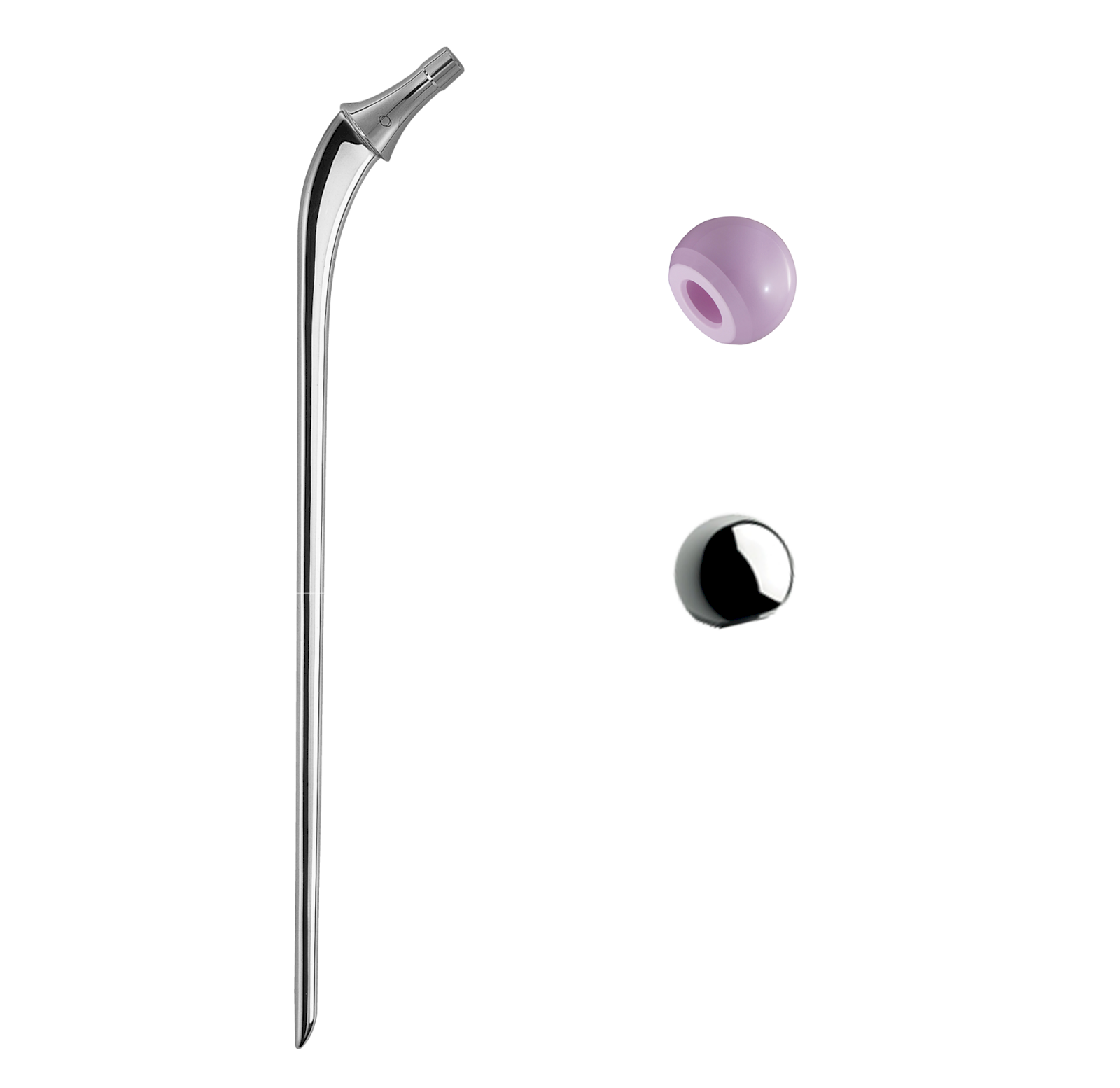





Revision INITIALE
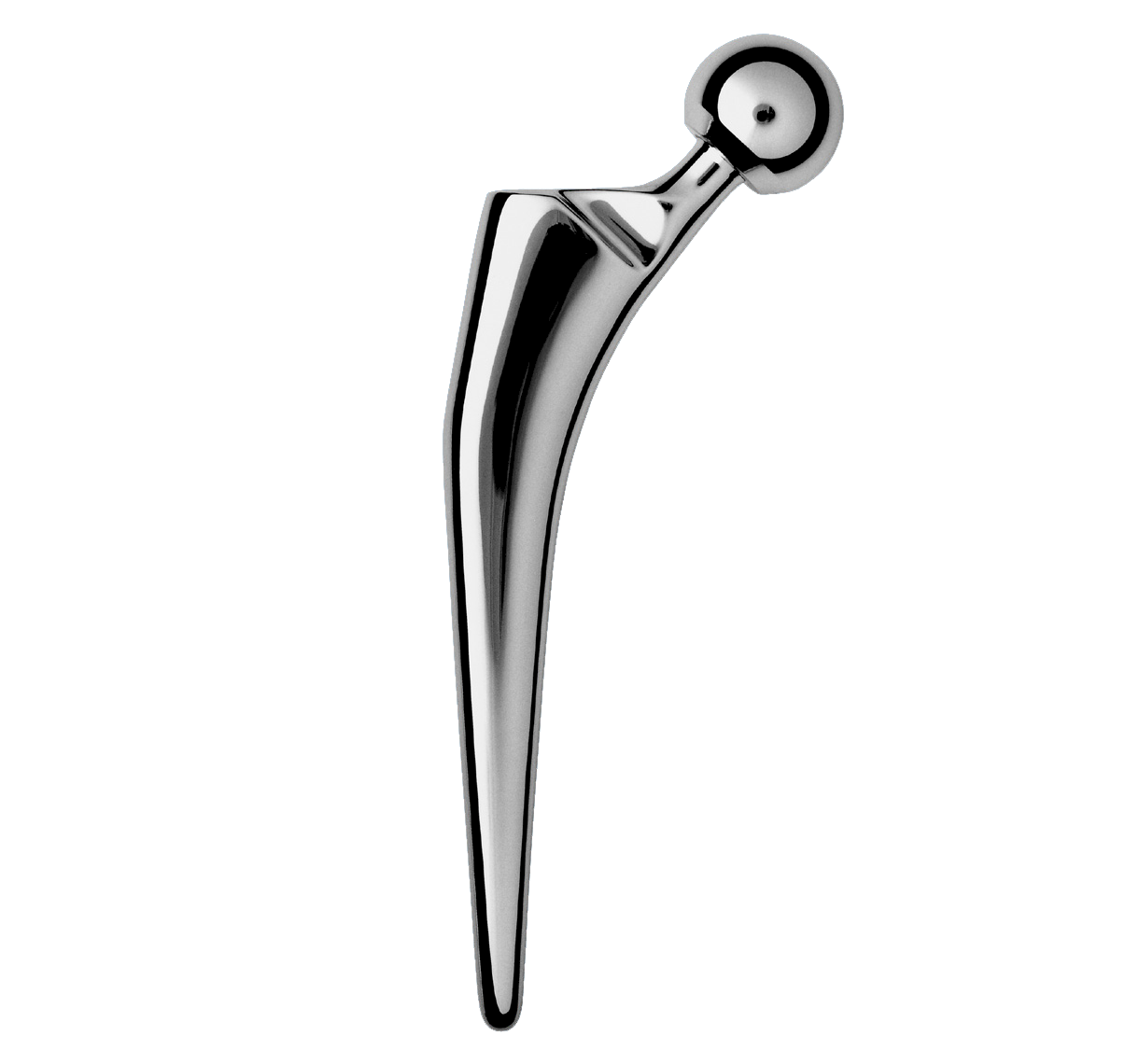
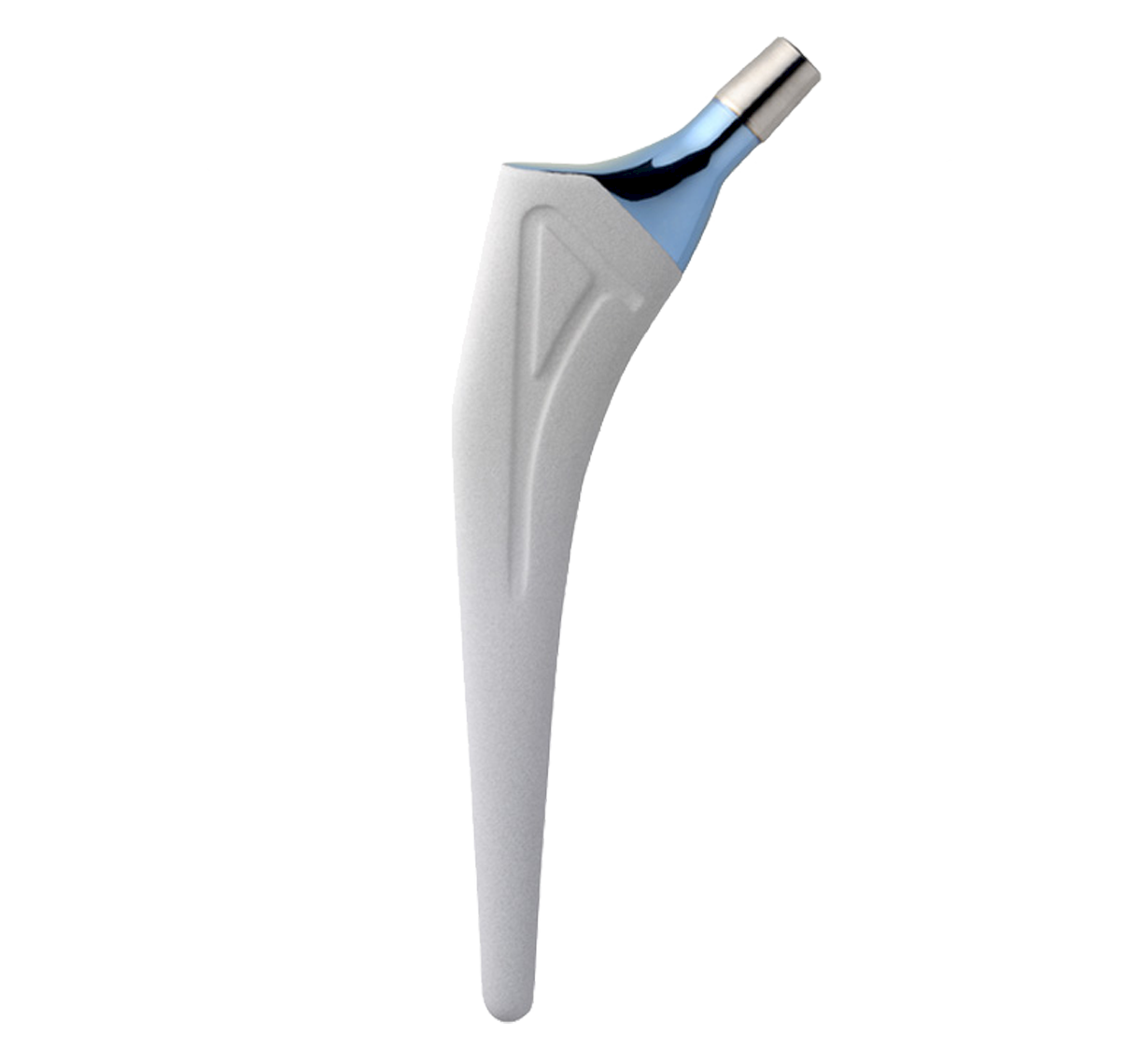
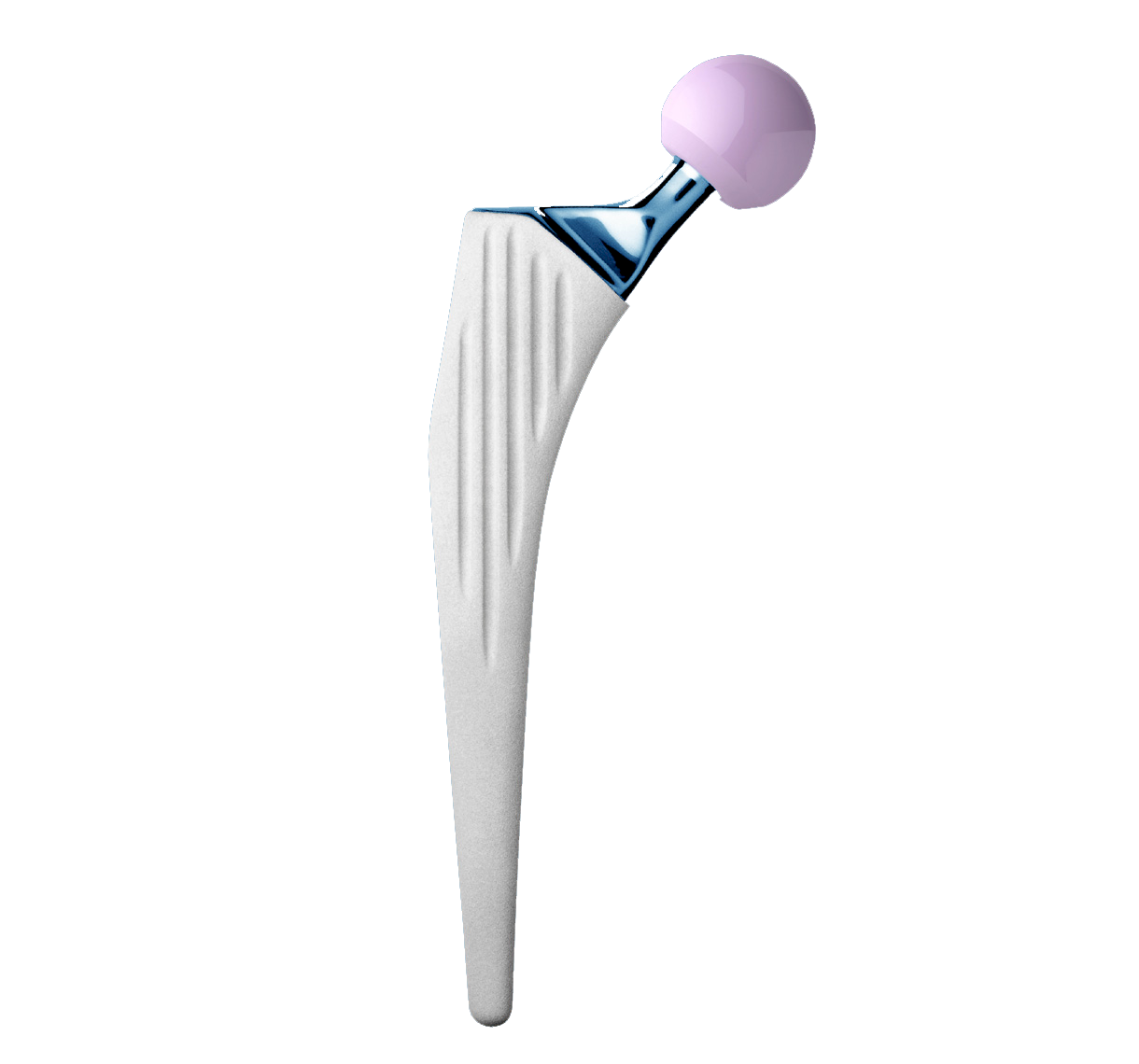
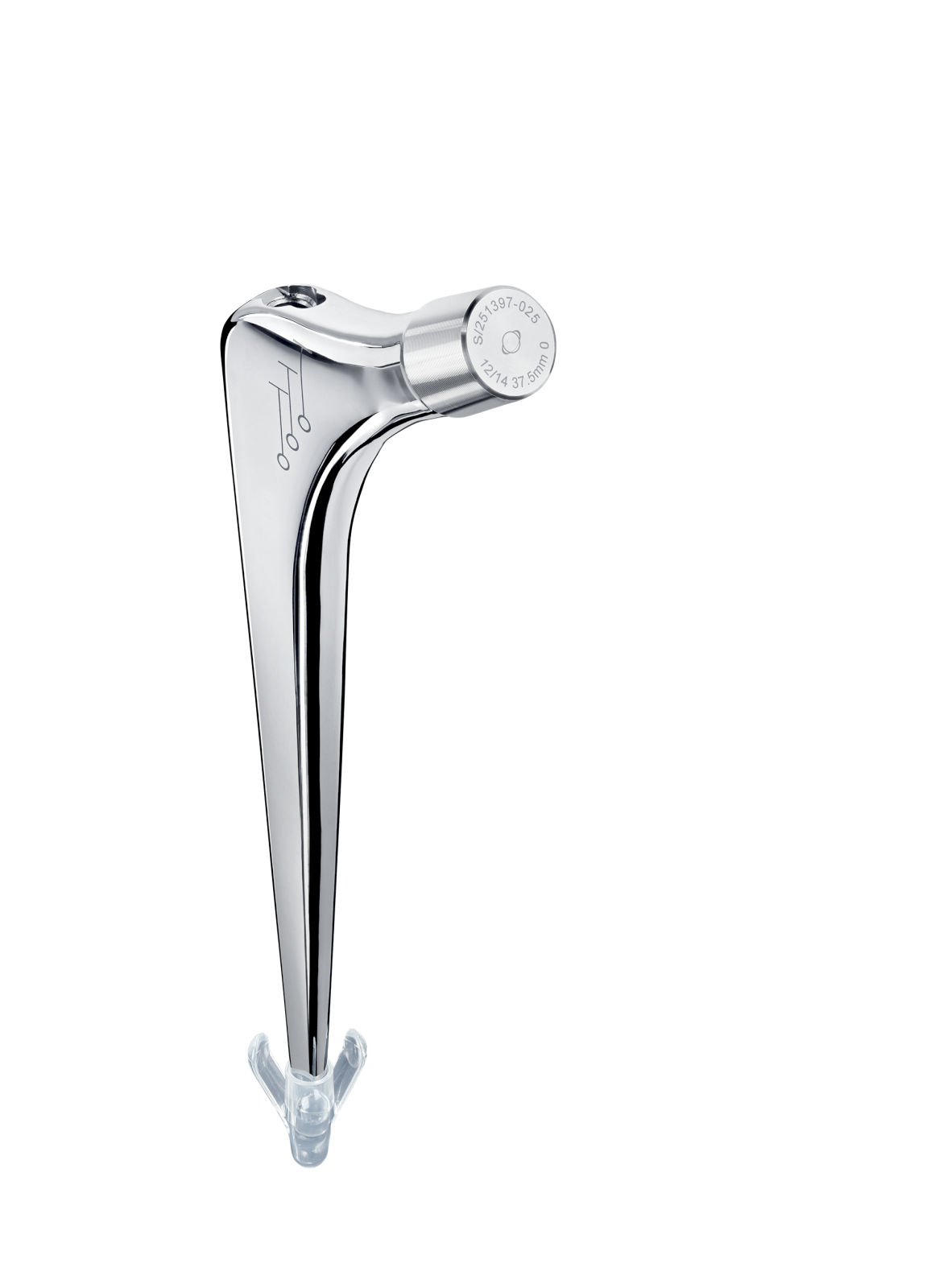
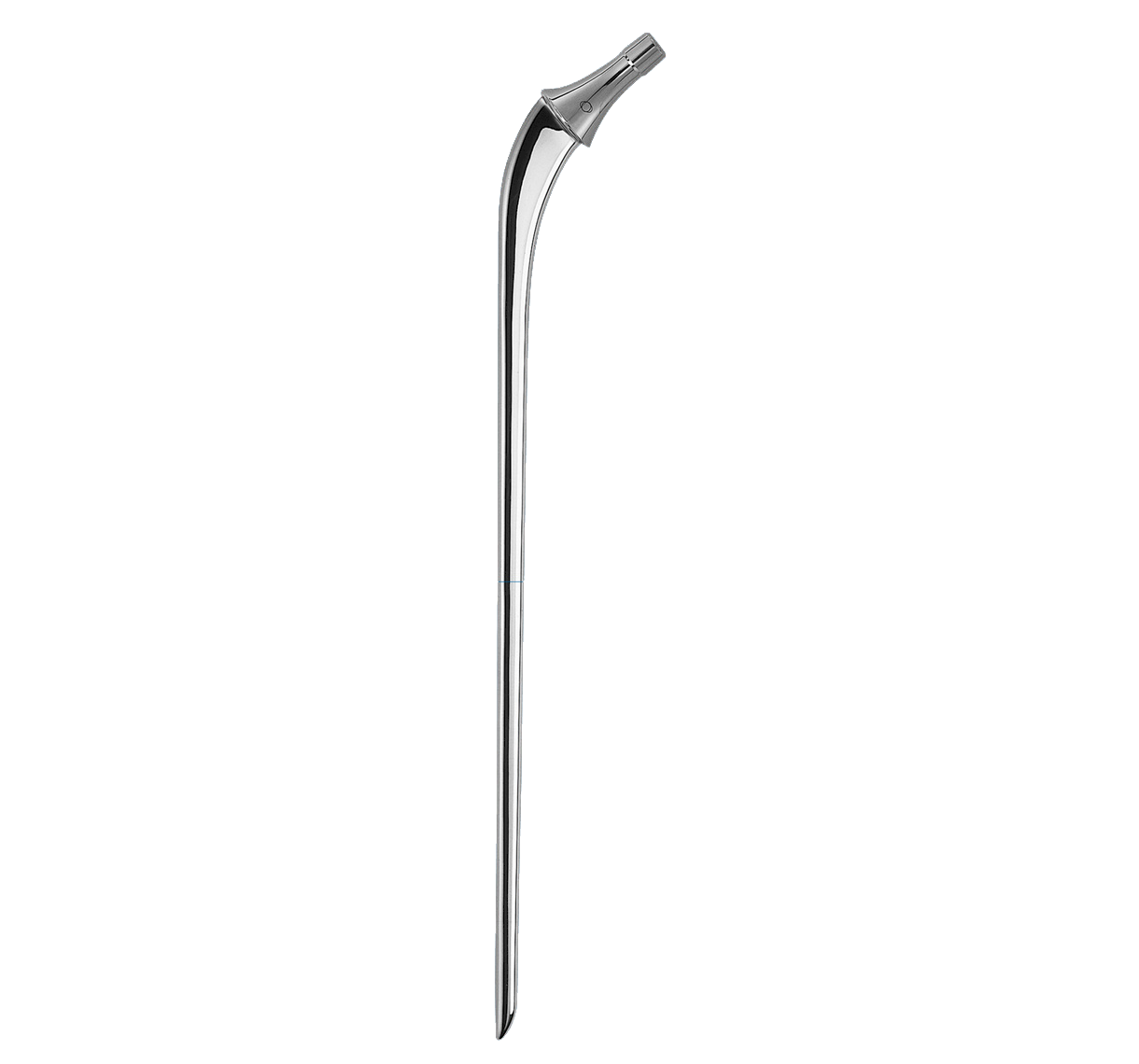
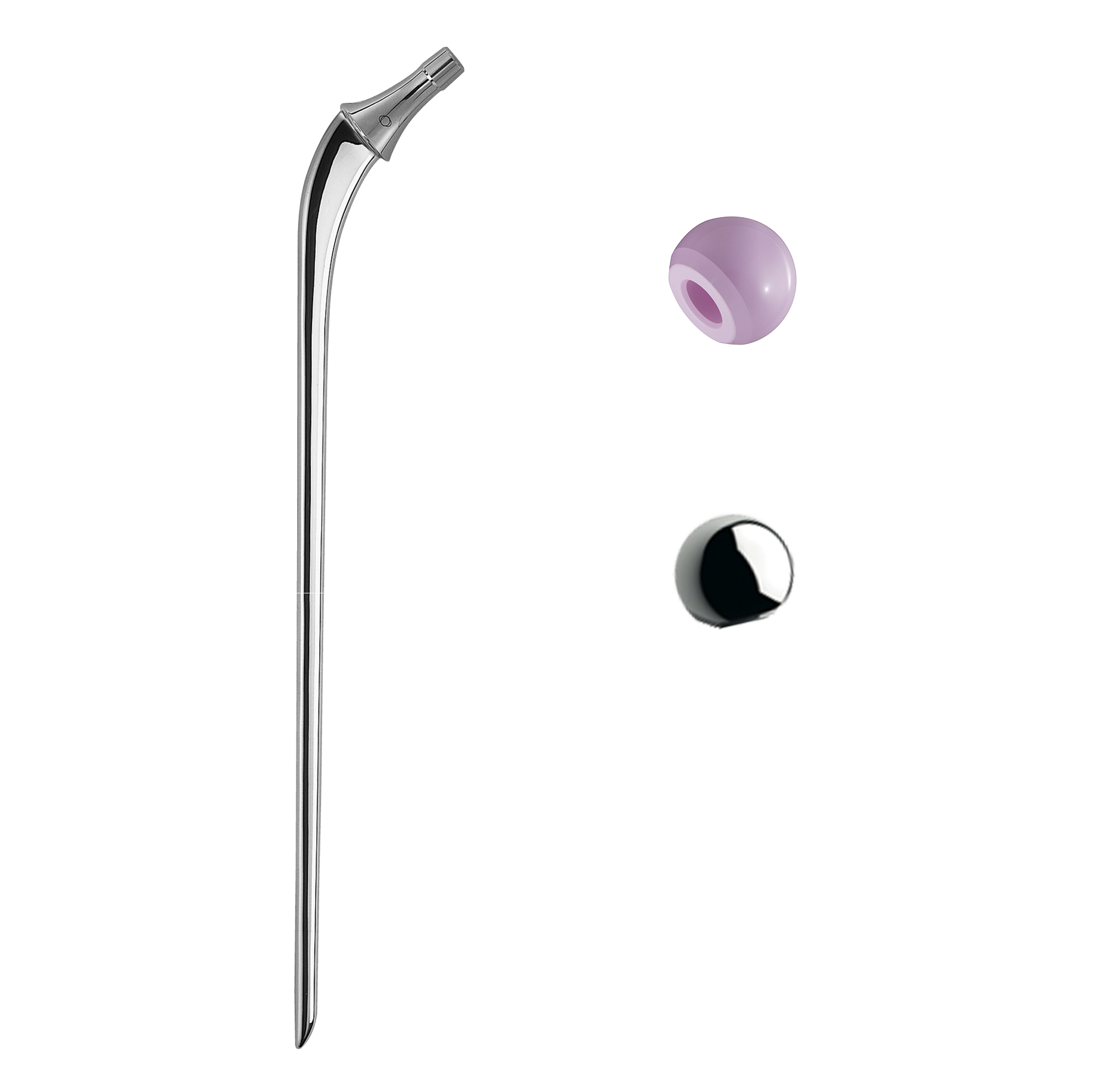
Revision straight femoral stems.
Design based on the benchmark cemented stem.
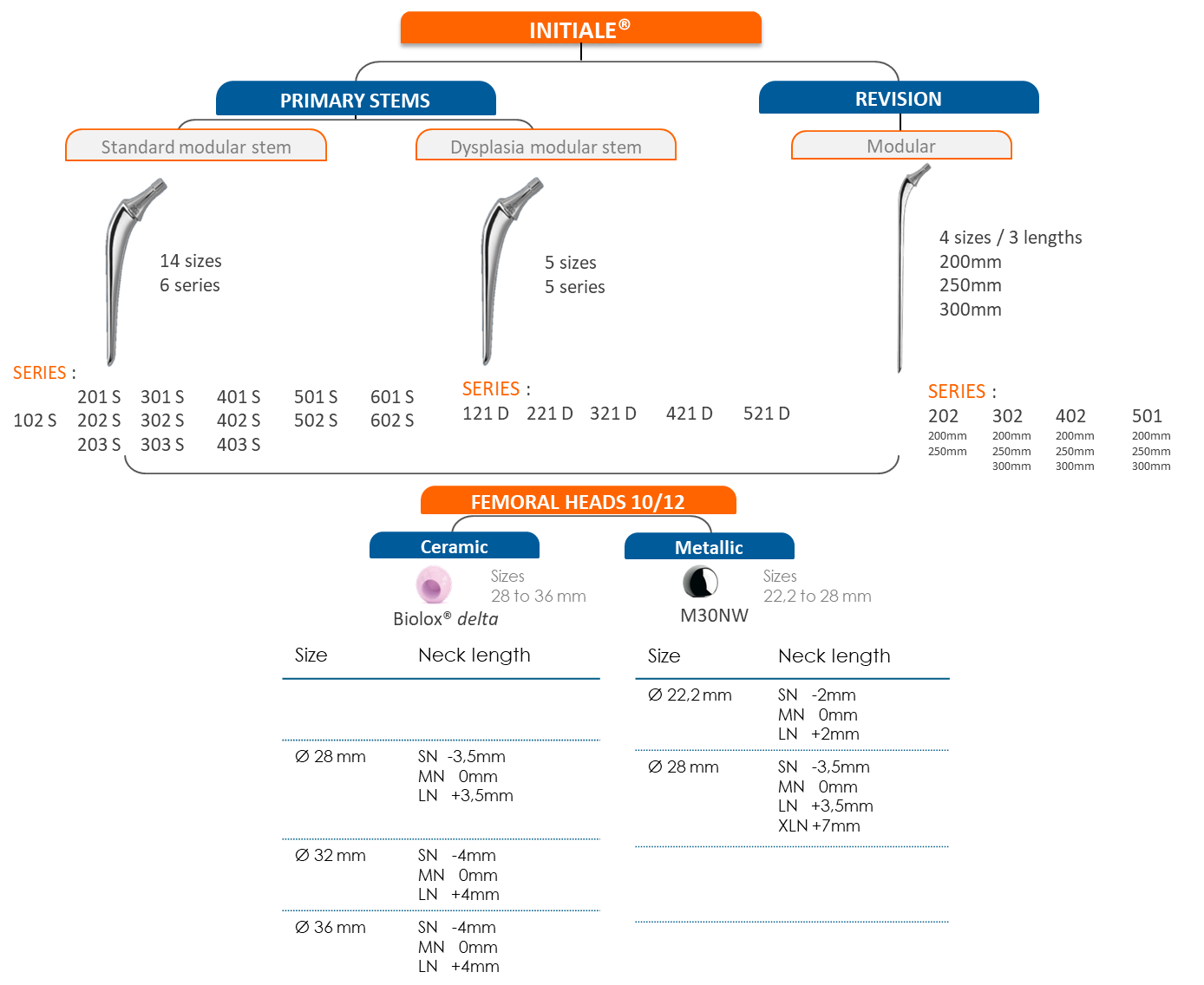
This stem product line consists of primary, revision and dysplasia stems.
In clinical use since 2000.
“Some devices may not be approved in your country, please contact your local distributor for further information”
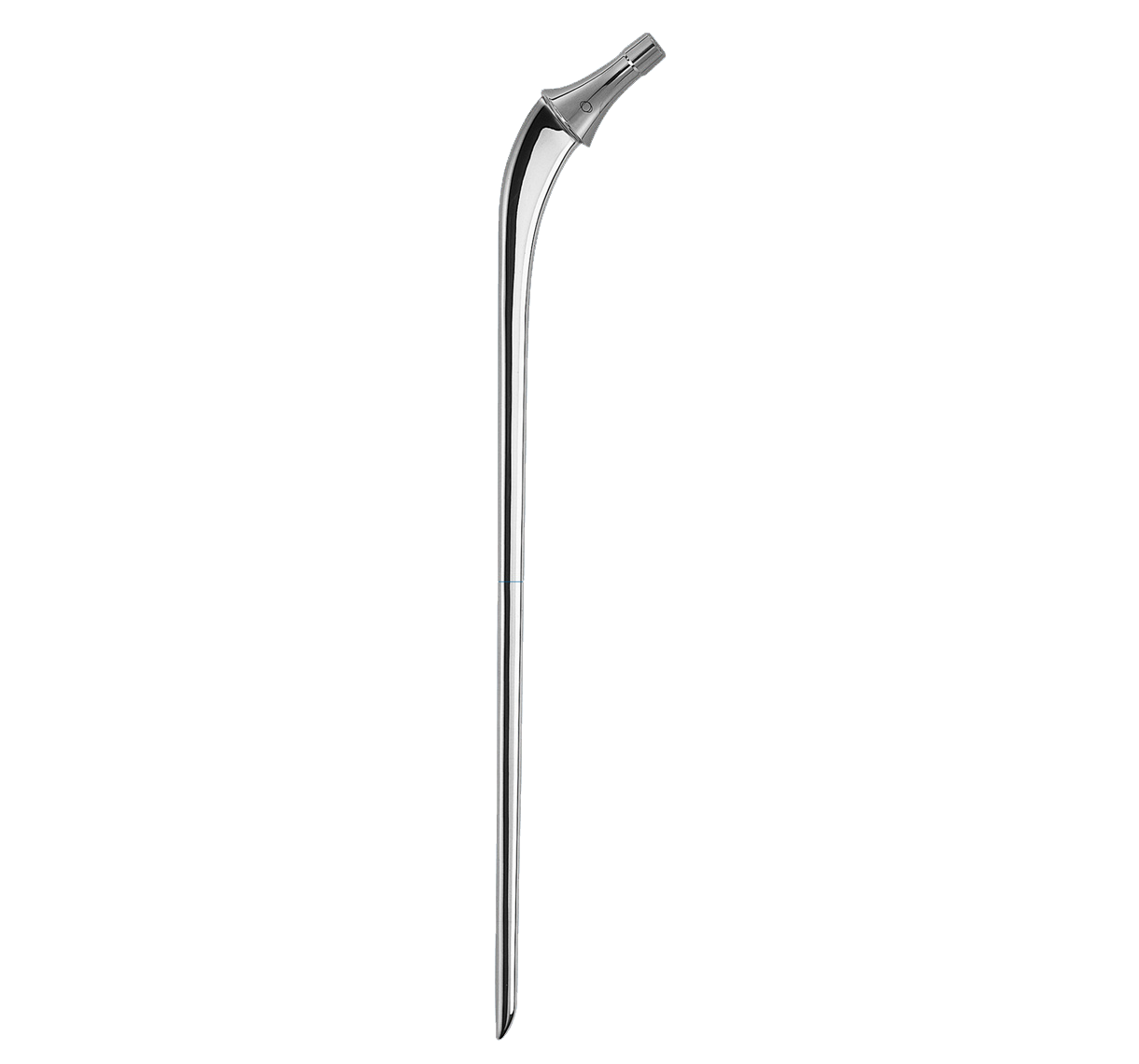
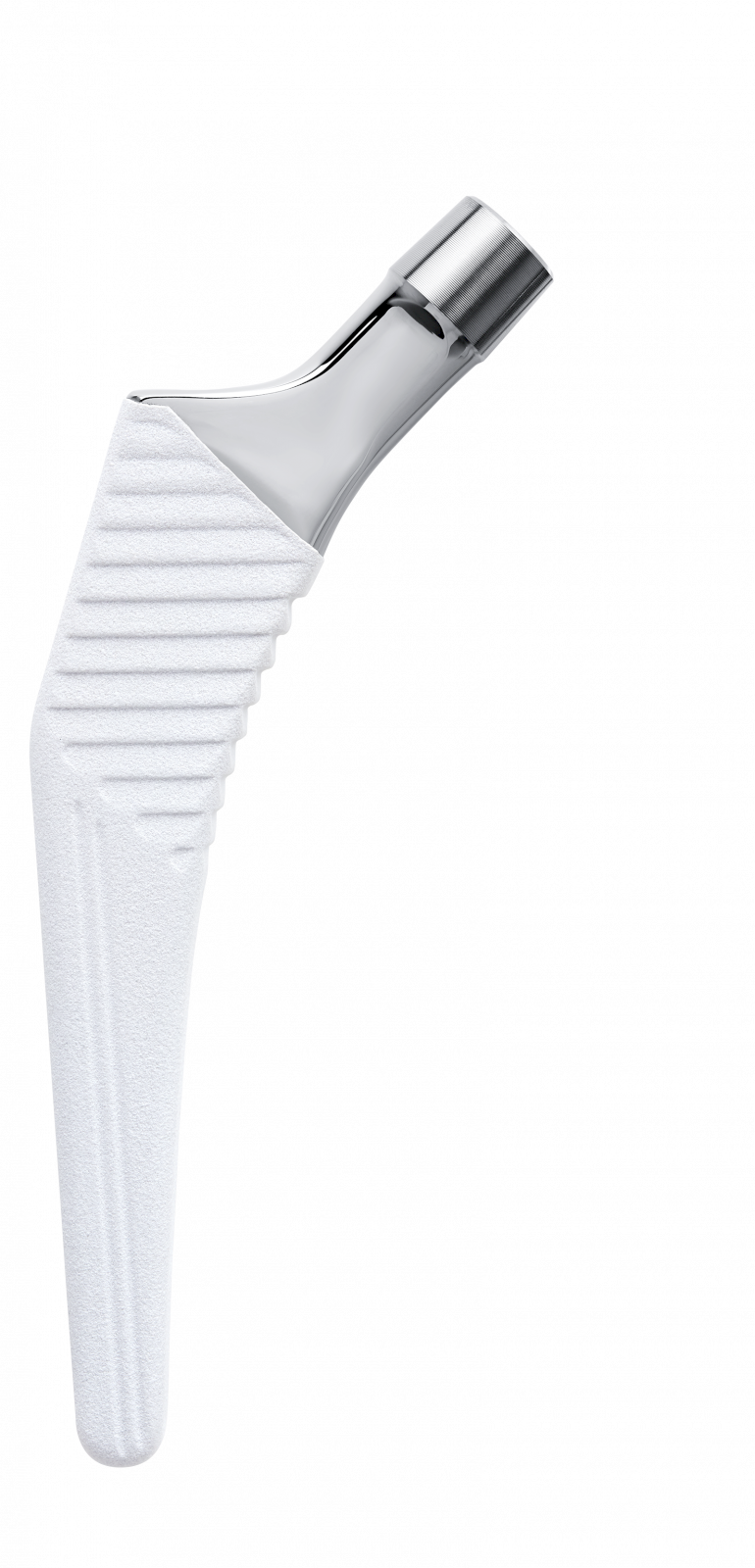
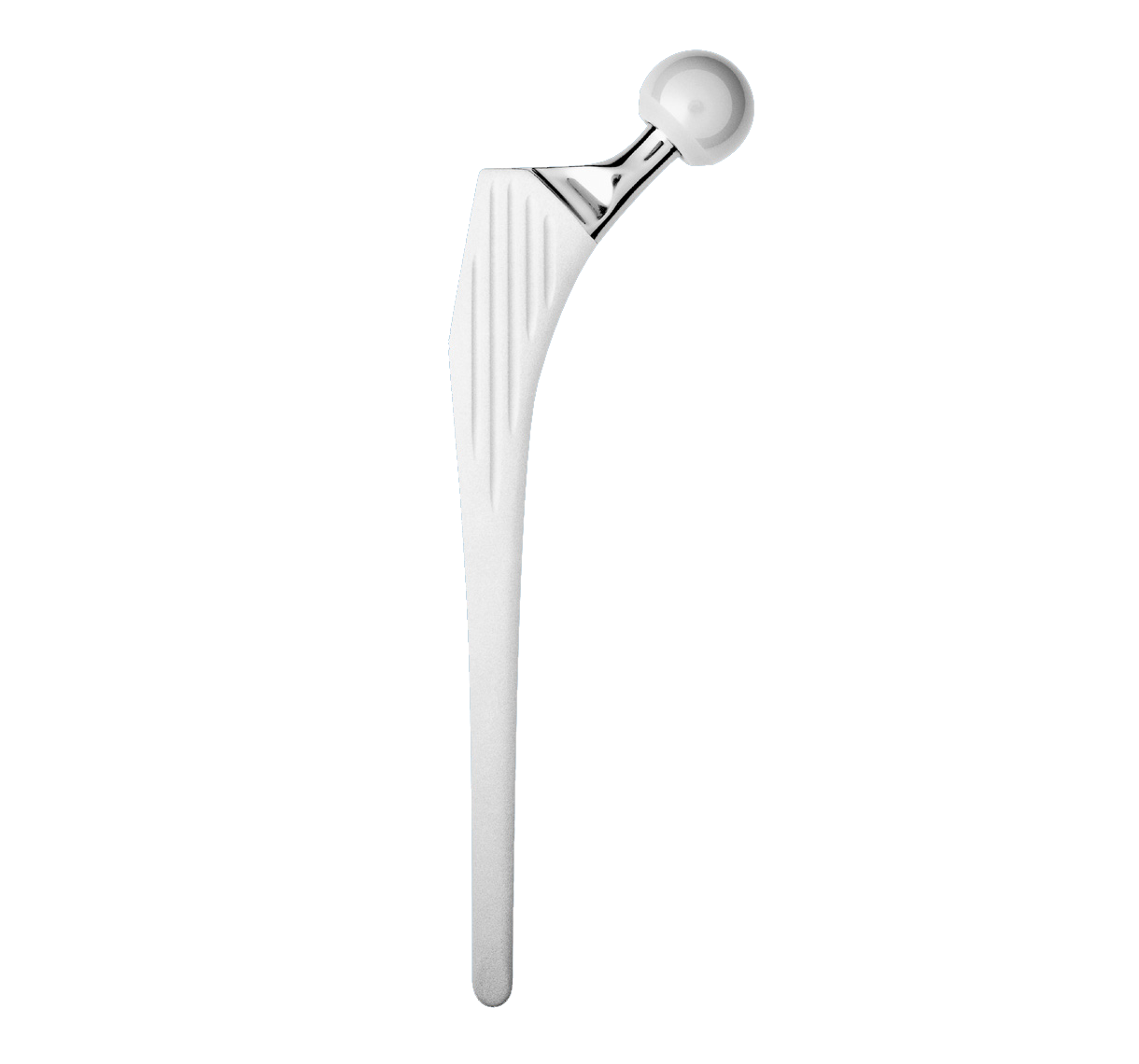
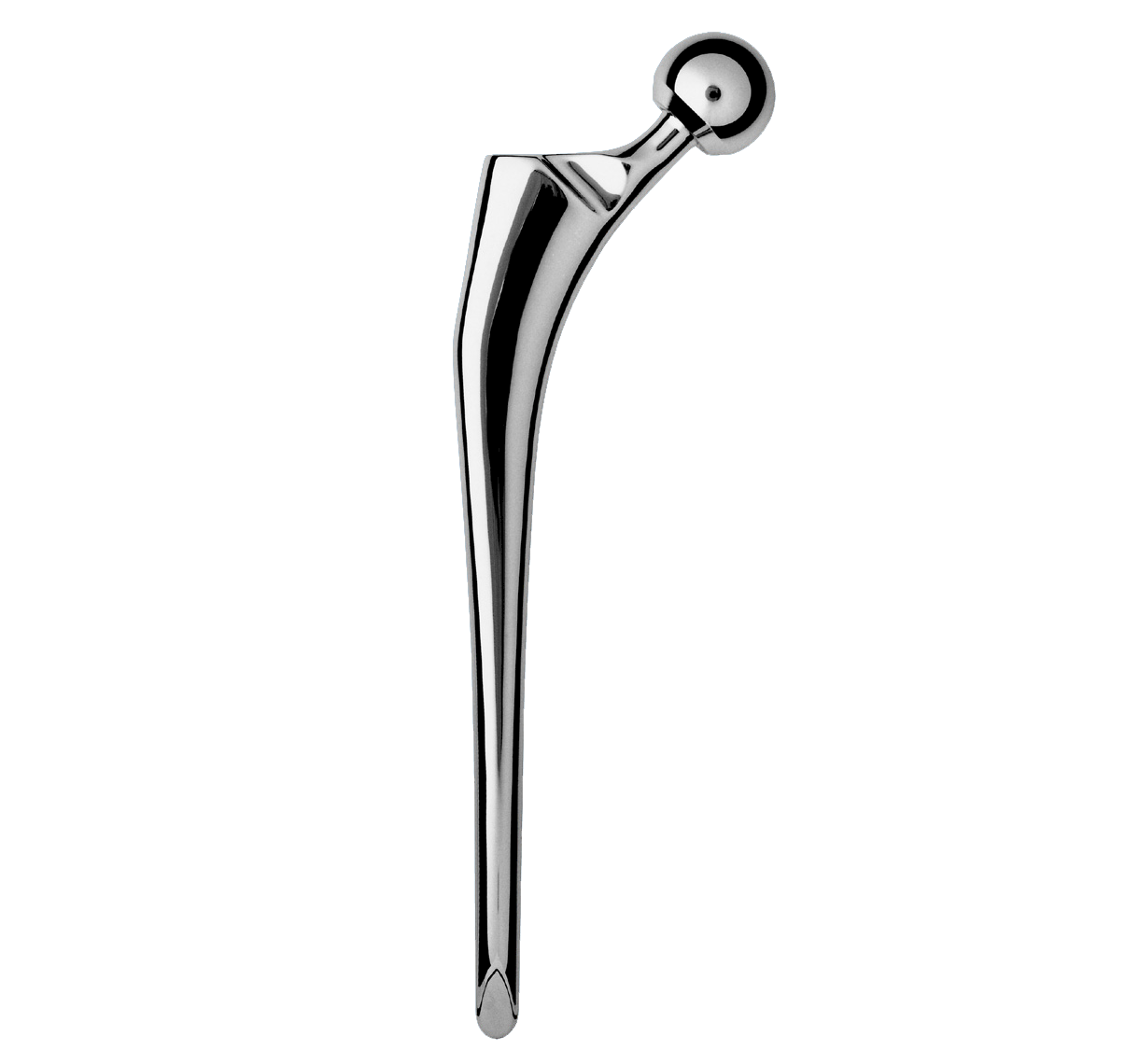
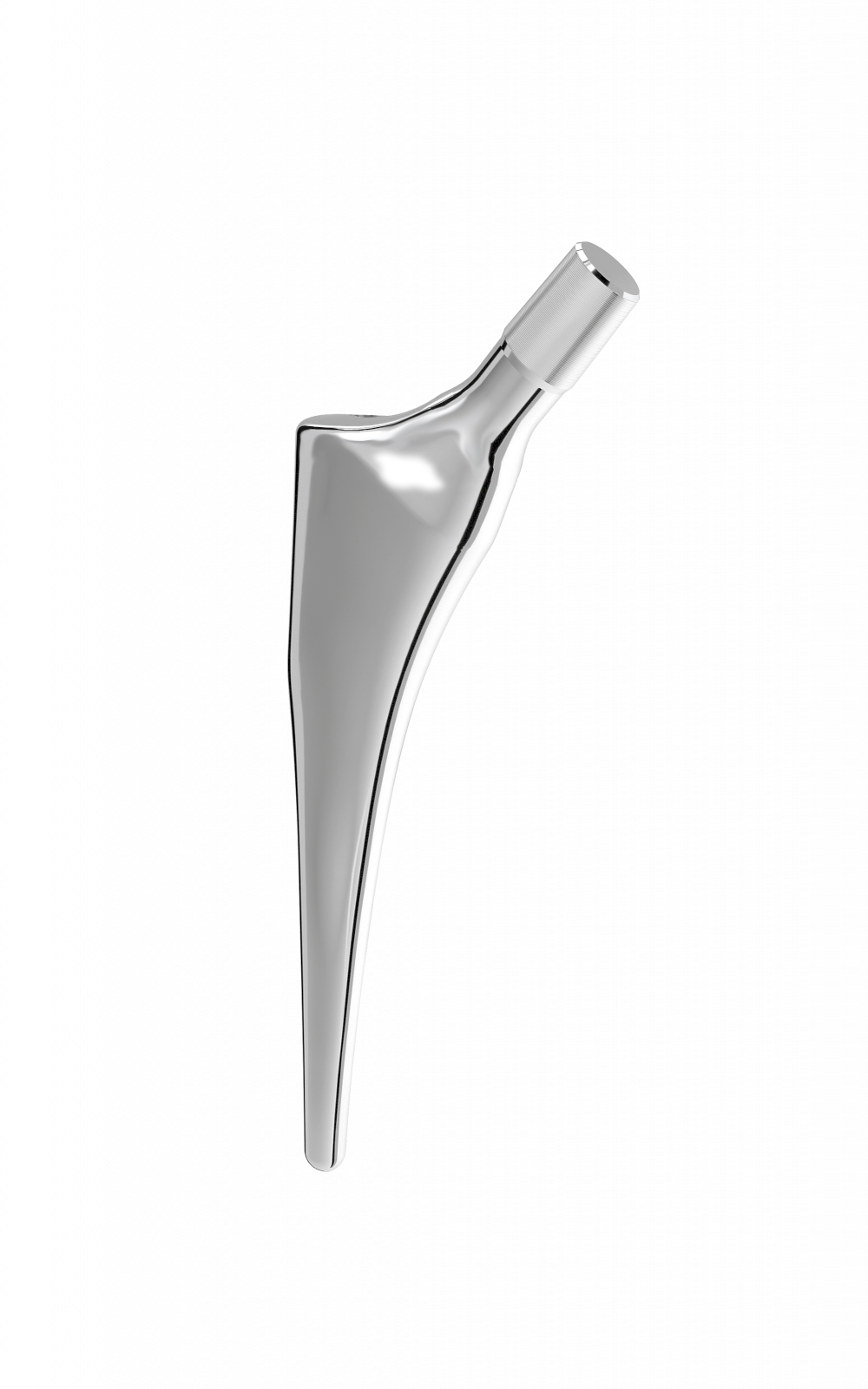
Entire stem has a highly polished finish to prevent abrasion of cement mantle (2).
Identical intramedullary shape to Primary INITIALE Stem. Only the length differs.
Different lengths within given size (see 'product range' tab).
Support collar.
Impaction hole on top of stem.
Material: stainless steel.
(2) T. Scheerlinck, P.-P. Casteleyn: The design features of cemented femoral hip implants.
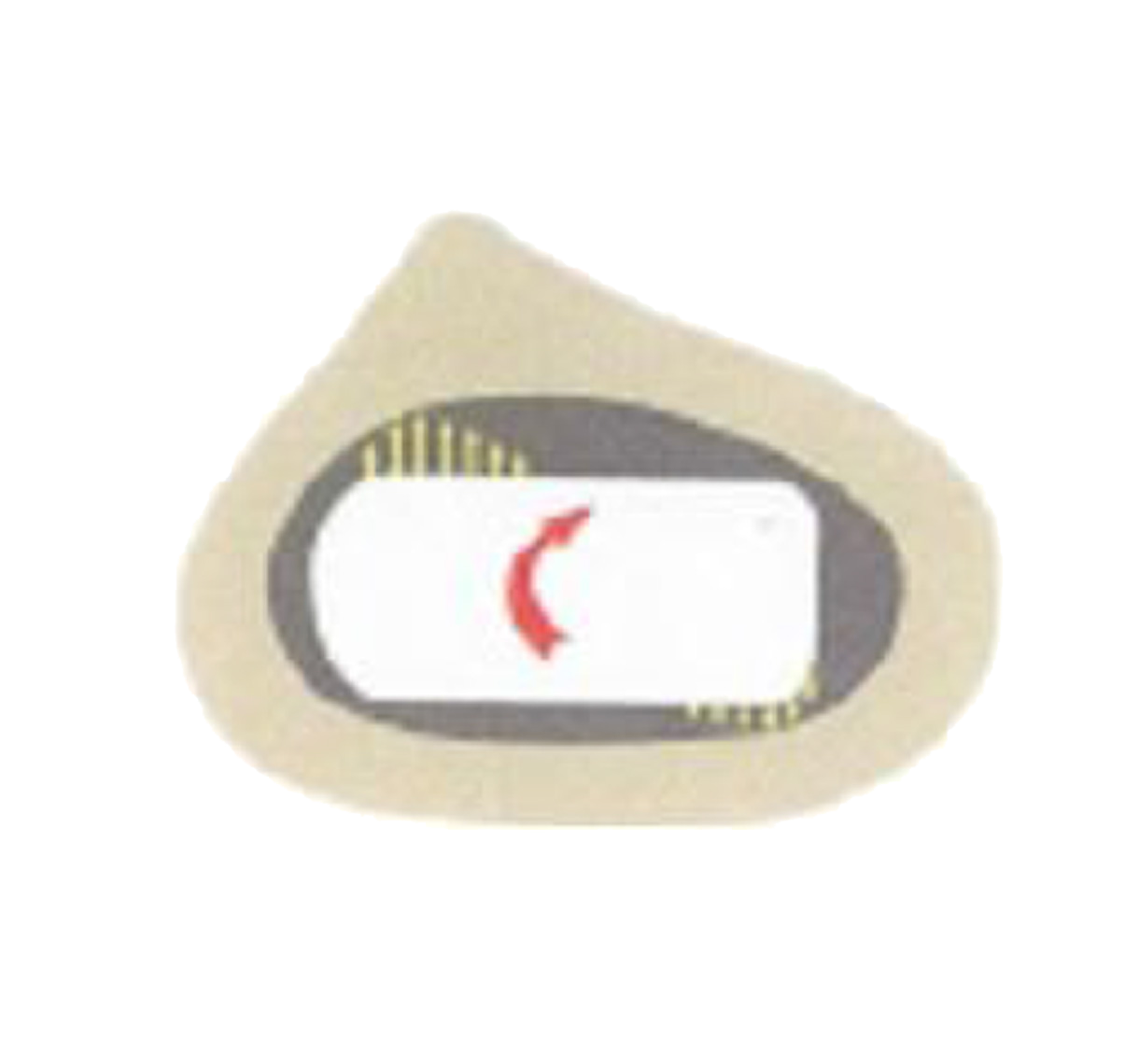
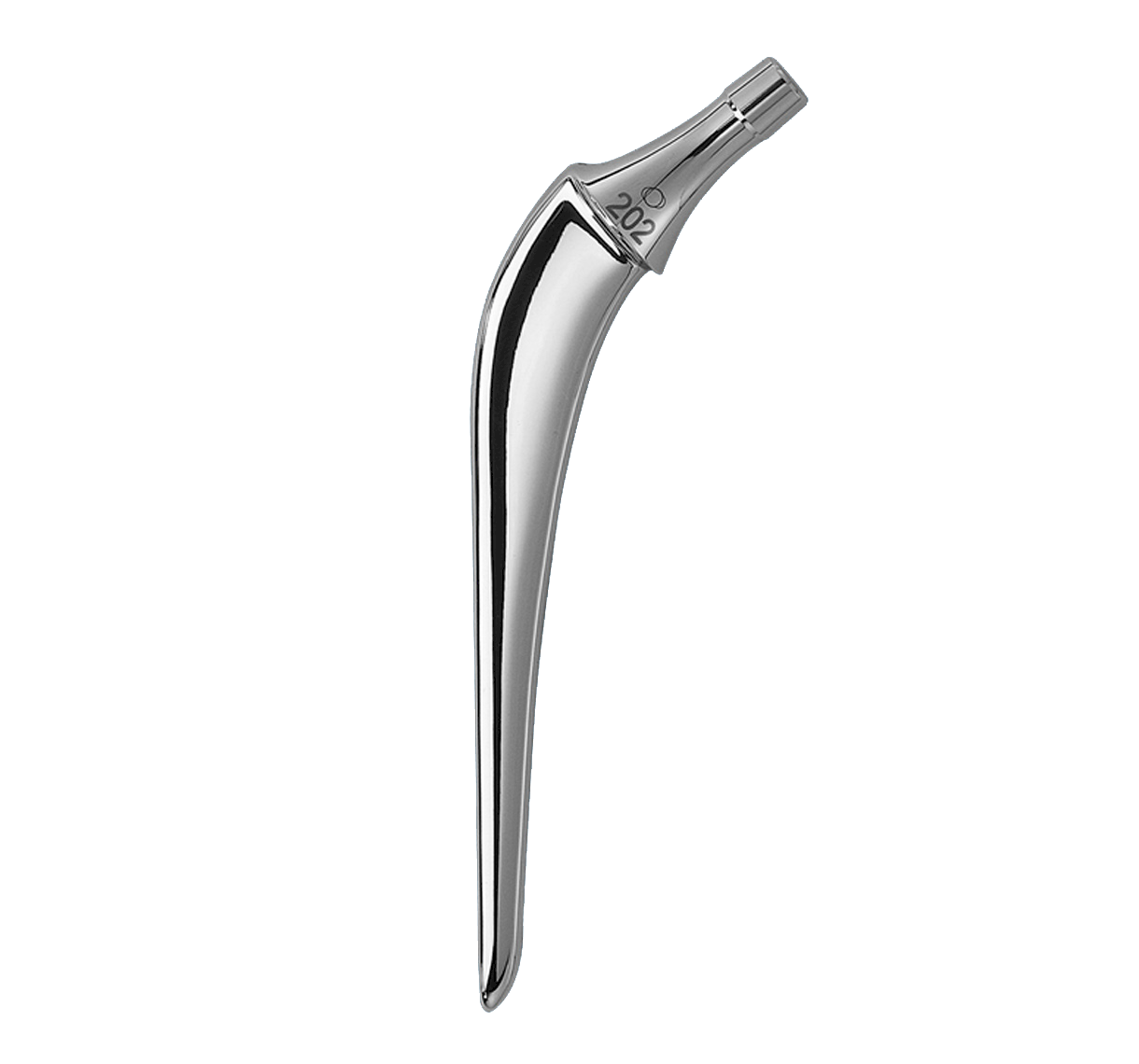
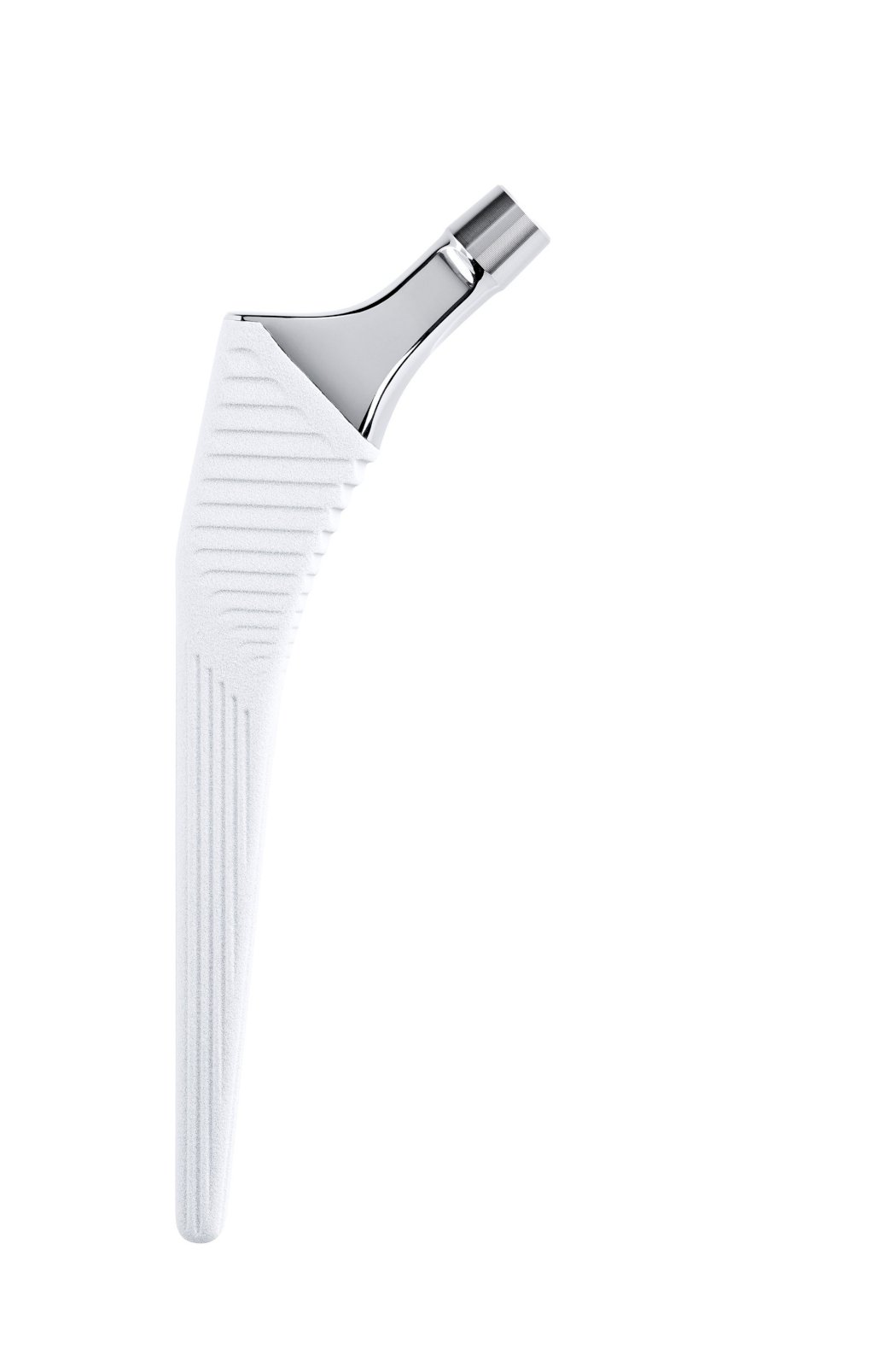
Rectangular stem shape transforms rotational shear loads into compressive forces (2).
Rounded edges prevent stress concentrations in the cement mantle.
(2) T. Scheerlinck, P.-P. Casteleyn: The design features of cemented femoral hip implants.
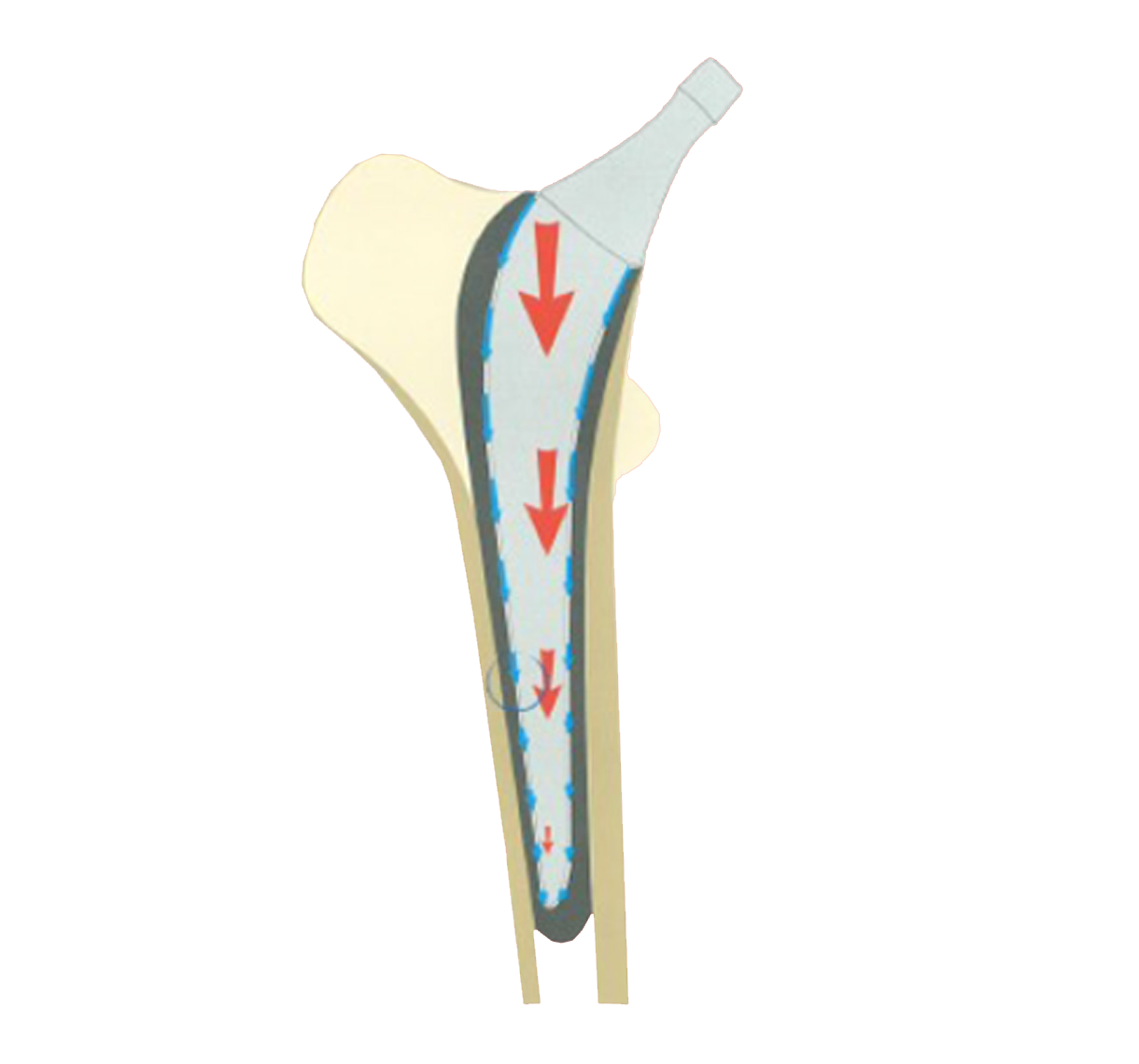
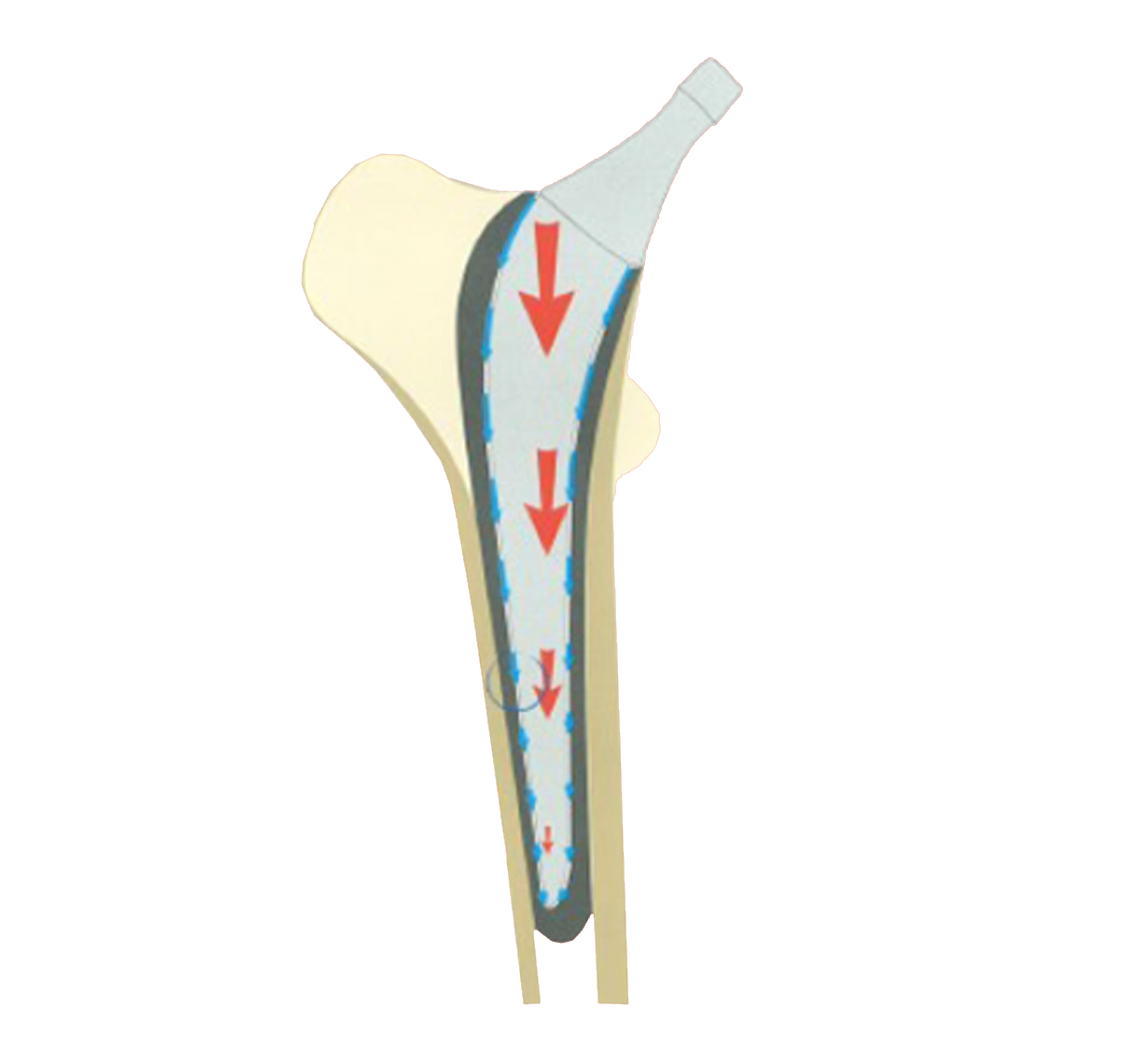
Tapered cross-section (A/P and lateral) helps to transform vertical loads into compressive forces (1).
Neck-shaft angle: 129° (average).
(1) New AM, Taylor M, Wroblewski BM: Effect of Hip Stem Taper on Cement Stresses.
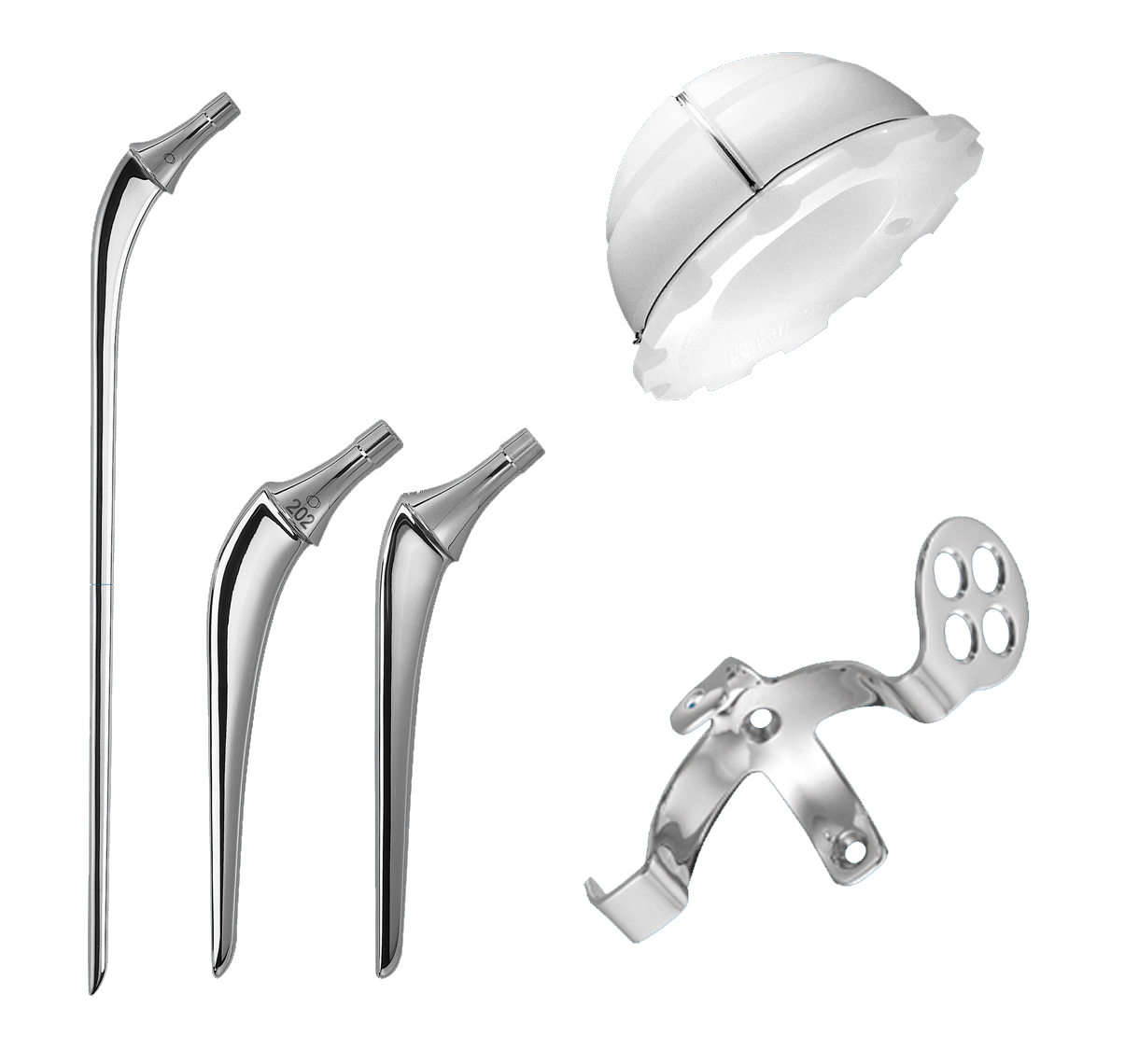

The INITIALE product line provides a comprehensive solution that remains faithful to the original concept:
INITIALE: cemented primary femoral stem that is also available in a dysplasia version.
INITIALE Revision: cemented revision femoral stem available in various lengths.
INITIALE Cup: cemented UHMWPE cup.
“Some devices may not be approved in your country, please contact your local distributor for further information”
Reconstruction cage: cemented acetabular. reconstruction cage.
Tapered cross-section (A/P and lateral) helps to transform vertical loads into compressive forces(1).
Neck-shaft angle: 129° (average).